Abstract
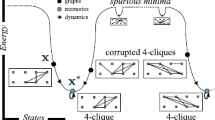
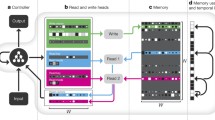
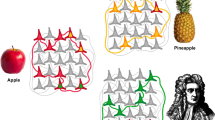
Artificial neural networks have been used as models of associative memory but their storage capacity is severely limited. Alternative machine-learning approaches perform better in classification tasks but require long learning sessions to build an optimized representational space. Here we present a radically new approach to the problem of classification based on the fact that networks associated to random hard constraint satisfaction problems display naturally an exponentially large number of attractor clusters. We introduce a warning propagation dynamics that allows selective mapping of arbitrary input vector onto these well-separated clusters of states, without need of training. The potential for such networks with exponential capacity to handle inputs with a combinatorially complex structure is finally explored with a toy-example.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopfield, J.J.: Neural Networks and Physical Systems with Emergent Collective Computational Abilities. Proc. Nat. Ac. Sci. 79, 2554–2558 (1982)
Amit, D.: Modeling Brain Function. Cambridge University Press, NY (1989)
Dubois, O., Monasson, R., Selman, B., Zecchina, R. (eds.): Theoretical Computer Science 265(1-2) (2001); Special issue on NP-hardness and phase transitions
Mézard, M., Zecchina, R.: Random K-Satisfiability: from an analytic solution to an efficient algorithm. Physical Review E 66, 056126 (2002)
Braunstein, A., Mézard, M., Zecchina, R.: Survey Propagation: an algorithm for satisfiability. Random Structures and Algorithms 27, 201–226 (2005)
Battaglia, D., Braunstein, A., Chavas, J., Zecchina, R.: Source coding by efficient probing of ground state clusters. Physical Review E 72, 015103 (2005)
Chavas, J., Battaglia, D., Cicutin, A., Zecchina, R.: Construction and VHDL Implementation of a Fully Local Network with Good Reconstruction Properties of the Inputs. In: Mira, J., Alvarez, J.R. (eds.) IWINAC 2005. LNCS, vol. 3562, pp. 385–394. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Krzakala, F., et al.: Gibbs states and the set of solutions of random constraint satisfaction problems. Proc. Nat. Ac. Sci. 104(25), 10318 (2007)
Montanari, A., Parisi, G., Ricci-Tersenghi, F.: Instability of one-step replica-simmetry-broken phase in satisfiability problems. Journal of Physics A 37, 2073 (2004)
Chavas, J., Furtlehner, C., Mézard, M., Zecchina, R.: Survey-propagation decimation through distributed local computations. Journ. Stat. Mech., P11016 (2005)
Fiser, J., Chiu, C., Weliki, M.: Small modulation of ongoing cortical dynamics by sensory input during natural vision. Nature 431, 573–578 (2004)
Dehaene, S., Naccache, L.: Towards a cognitive neuroscience of consciousness: basic evidence and a workspace framework. Cognition 79, 1–37 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Battaglia, D. (2009). Neuron-Less Neural-Like Networks with Exponential Association Capacity at Tabula Rasa . In: Mira, J., Ferrández, J.M., Álvarez, J.R., de la Paz, F., Toledo, F.J. (eds) Methods and Models in Artificial and Natural Computation. A Homage to Professor Mira’s Scientific Legacy. IWINAC 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5601. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02264-7_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02264-7_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02263-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02264-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)