Abstract
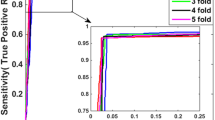
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) prediction is one of the main goals in the current Proteomics. This work presents a method for prediction of protein-protein interactions through a classification technique known as Support Vector Machines. The dataset considered is a set of positive and negative examples taken from a high reliability source, from which we extracted a set of genomic features, proposing a similarity measure. Feature selection was performed to obtain the most relevant variables through a modified method derived from other feature selection methods for classification. Using the selected subset of features, we constructed a support vector classifier that obtains values of specificity and sensitivity higher than 90% in prediction of PPIs, and also providing a confidence score in interaction prediction of each pair of proteins.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Hur, A., Noble, W.S.: Kernel methods for predicting protein-protein interactions. Bioinformatics (2005)
Bork, P., et al.: Protein interaction networks from yeast to human. Current Opinion in Structural Biology (2004)
Vapnik, V., Cortes, C.: Support vector network. Mach. Learn. (1995)
Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene ontology (go) database and informatics resource. Nucl. Acids Res. (2004)
Craig, L.L.: Improving protein protein interaction prediction based on phylogenetic information using a least-squares support vector machine. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci (2007)
Berman, H.M., et al.: The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. (2000)
Boeckmann, B., et al.: The swiss-prot protein knowledgebase and its supplement trembl in 2003. Nucleic Acids Research (2003)
Camon, E., et al.: The gene ontology annotation (goa) database: sharing knowledge in uniprot with gene ontology. Nucleic Acids Research (2004)
Güldener, U., et al.: Cygd: the comprehensive yeast genome database. Nucleic Acids Research (2005)
Jansen, R., et al.: A bayesian networks approach for predicting protein-protein interactions from genomic data. Science (2003)
Wu, X., et al.: Prediction of yeast protein-protein interaction network: insights from gene ontology and annotations. Nucleic Acids Research (2006)
Herrera, L.J., Pomares, H., Rojas, I., Guillén, A., Prieto, A., Valenzuela, O.: Recursive prediction for long term time series forecasting using advanced models. Neurocomputing 70, 2870–2880 (2007)
Herrera, L.J., Pomares, H., Rojas, I., Valenzuela, O., Prieto, A.: Tase, a taylor series based fuzzy system model that combines interpretability and accuracy. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 153, 403–427 (2005)
Kira, K., Rendell, L.: A practical approach to feature selection. In: Proc. 9th International Workshop on Machine Learning (1992)
Patil, A., Nakamura, H.: Filtering high-throughtput protein-protein interaction data using a combination of genomic features. BMC Bioinformatics (2005)
Nakamura, H., Hint, P.A.: A database of annoted protein-protein interactions and their homologs. Biophysics (2005)
Gilad-Bachrach, A.N.R., Tishby, N.: Margin based feature selection: Theory and algorithms. In: Proc. of the 21’st ICML (2004)
Rojas, I., Pomares, H., Gonzáles, J., Bernier, J.L., Ros, E., Pelayo, F.J., Prieto, A.: Analysis of the functional block involved in the design of radial basis function networks. Neural Process. Lett. 12(1), 1–17 (2000)
Saeed, R., Deane, C.: An assessment of the uses of homologous interactions. Bioinformatics Advance Access (2007)
Aloy, P., Stein, A., Russell, R.B.: 3did: interacting protein domains of known three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res. (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Urquiza, J.M. et al. (2009). Method for Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions in Yeast Using Genomics/Proteomics Information and Feature Selection. In: Cabestany, J., Sandoval, F., Prieto, A., Corchado, J.M. (eds) Bio-Inspired Systems: Computational and Ambient Intelligence. IWANN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5517. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02478-8_107
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02478-8_107
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02477-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02478-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)