Abstract
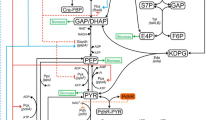
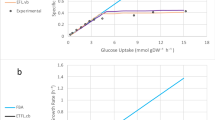
The major objective of metabolic engineering is the construction of industrially relevant microbial strains with desired properties. From an engineering perspective, dynamic mathematical modeling to quantitatively assess intracellular metabolism and predict the complex behavior of living cells is one of the most successful tools to achieve that goal. In this work, we present an expansion of the original E. coli dynamic model [1], which links the acetate metabolism and tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) with the phosphotransferase systems, the pentose-phosphate pathway and the glycolysis system based on mechanistic enzymatic rate equations. The kinetic information is collected from available database and literature, and is used as an initial guess for the global fitting. The results of the numeric simulations were in good agreement with the experimental results. Thus, the results are sufficiently good to prompt us to seek further experimental data for comparison with the simulations.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chassagnole, C., Noisommit-Rizzi, N., Schmid, J.W., Mauch, K., Reuss, M.: Dynamic modeling of the central carbon metabolism of Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 79, 53–73 (2002)
Dairaku, K., Izumoto, E., Morikawa, H., Shioya, S., Takamatsu, T.: Optimal quality control of Baker’s yeast fed-batch culture using population dynamics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24, 2661–2674 (1982)
Blanch, H.W.: Microbial growth kinetics. Chem. Eng. Commun. 8, 181–211 (1981)
Gombert, A.K., Nielsen, J.: Mathematical modelling of metabolism. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 11, 180–186 (2000)
Varner, J.D.: Large-scale prediction of phenotype: Concept. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 69, 664–678 (2000)
Chassagnole, C., Rais, B., Quentin, E., Fell, D.A., Mazat, J.P.: An integrated study of threonine-pathway enzyme kinetics in Escherichia coli. Biochemical Journal 356, 415–423 (2001)
Wittig, U., Golebiewski, M., Kania, R., Krebs, O., Mir, S., Weidemann, A., Ansteins, S., Saric, J., Rojas, I.: SABIO-RK: Integration and curation of reaction kinetic data. In: Leser, U., Naumann, F., Eckman, B. (eds.) DILS 2006. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 4075, pp. 94–103. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Sundararaj, S., Guo, A., Habibi-Nazhad, B., Rouani, M., Stothard, P., Ellison, M., Wishart, D.S.: The CyberCell Database (CCDB): a comprehensive, self-updating, relational database to coordinate and facilitate in silico modeling of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research 32, D293–D295 (2004)
Bakker, B.M., Michels, P.A.M., Opperdoes, F.R., Westerhoff, H.V.: Glycolysis in bloodstream form Trypanosoma brucei can be understood in terms of the kinetics of the glycolytic enzymes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272, 3207–3215 (1997)
Henkin, J., Abeles, R.H.: Evidence against an Acyl-enzyme intermediate in reaction catalyzed by Clostridial phosphotransacetylase. Biochemistry 15, 3472–3479 (1976)
Karp, P., Riley, M., Saier, M., Paulsen, I.T., Paley, S.M., Pellegrini-Toole, A.: The EcoCyc and MetaCyc databases. Nucleic Acids Research 28, 56–59 (2000)
Zhao, J., Shimizu, K.: Metabolic flux analysis of Escherichia coli K12 grown on C-13-labeled acetate and glucose using GG-MS and powerful flux calculation method. Journal of Biotechnology 101, 101–117 (2003)
Tian, J., Bryk, R., Itoh, M., Suematsu, M., Nathan, C.: Variant tricarboxylic acid cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Identification of alpha-ketoglutarate decarboxylase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102, 10670–10675 (2005)
Hoefnagel, M.H.N., Starrenburg, M.J.C., Martens, D.E., Hugenholtz, J., Kleerebezem, M., Van Swam, I.I., Bongers, R., Westerhoff, H.V., Snoep, J.L.: Metabolic engineering of lactic acid bacteria, the combined approach: kinetic modelling, metabolic control and experimental analysis. Microbiology-Sgm 148, 1003–1013 (2002)
Walsh, K., Koshland, D.E.: Branch Point Control by the Phosphorylation State of Isocitrate Dehydrogenase - A Quantitative Examination of Fluxes During A Regulatory Transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 260, 8430–8437 (1985)
Schomburg, I., Chang, A., Schomburg, D.: BRENDA, enzyme data and metabolic information. Nucleic Acids Research 30, 47–49 (2002)
Ishii, N., Nakahigashi, K., Baba, T., Robert, M., Soga, T., Kanai, A., Hirasawa, T., Naba, M., Hirai, K., Hoque, A., Ho, P.Y., Kakazu, Y., Sugawara, K., Igarashi, S., Harada, S., Masuda, T., Sugiyama, N., Togashi, T., Hasegawa, M., Takai, Y., Yugi, K., Arakawa, K., Iwata, N., Toya, Y., Nakayama, Y., Nishioka, T., Shimizu, K., Mori, H., Tomita, M.: Multiple high-throughput analyses monitor the response of E-coli to perturbations. Science 316, 593–597 (2007)
Hoque, M.A., Ushiyama, H., Tomita, M., Shimizu, K.: Dynamic responses of the intracellular metabolite concentrations of the wild type and pykA mutant Escherichia coli against pulse addition of glucose or NH3 under those limiting continuous cultures. Biochemical Engineering Journal 26, 38–49 (2005)
Goldberg, R.N., Tewari, Y.B., Bhat, T.N.: Thermodynamics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions - a database for quantitative biochemistry. Bioinformatics 20, 2874–2877 (2004)
Hoops, S., Sahle, S., Gauges, R., Lee, C., Pahle, J., Simus, N., Singhhal, M., Xu, L., Mendes, P., Kummer, U.: COPASI — a COmplex PAthway SImulator. Bioinformatics 22, 3067–3074 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Costa, R.S., Machado, D., Rocha, I., Ferreira, E.C. (2009). Large Scale Dynamic Model Reconstruction for the Central Carbon Metabolism of Escherichia coli . In: Omatu, S., et al. Distributed Computing, Artificial Intelligence, Bioinformatics, Soft Computing, and Ambient Assisted Living. IWANN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5518. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02481-8_163
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02481-8_163
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02480-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02481-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)