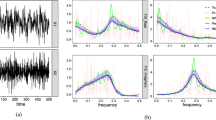
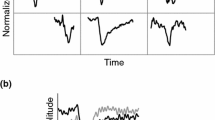
Abstract
Bump modeling is a method used to extract oscillatory bursts in electrophysiological signals, who are most likely to be representative of local synchronies. In this paper we present an improved sparse bump modeling method. The improvements are done in the adaptation method by optimizing the parameters according to the order of their derivatives; and in the window matching method by changing the selection of the initial function. Experimental results, comparing previous method vs the improved version, show that the obtained model fits better the signal, hence the result will be much more precise and useful.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Başar, E.: EEG-brain dynamics: Relation between EEG and brain evoked potentials. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1980)
Başar, E., Demilrap, T., Schürmann, M., Başar-Eroglu, C., Ademoglu, A.: Oscillatory brain dynamics, wavelet analysis, ands cognition. Brain and Language 66, 146–183 (1999)
Buscema, M., Rossini, P., Babiloni, C., Grossi, E.: The ifast model, a novel parallel nonlinear eeg analysis technique, distinguishes mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease patients with high degree of accuracy. Artificial Intelligence In Medicine 40, 127–141 (2007)
Dauwels, J., Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A.: A novel measure for synchrony and its application to neural signals. In: Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2007), Honolulu, USA, April 15-20, vol. IV, pp. 1165–1168 (2007)
Dauwels, J., Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A.: On synchrony measures for the detection of alzheimer’s disease based on eeg. In: Ishikawa, M., Doya, K., Miyamoto, H., Yamakawa, T. (eds.) ICONIP 2007, Part I. LNCS, vol. 4984, pp. 112–125. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Dauwels, J., Vialatte, F., Rutkowski, T.M., Cichocki, A.: Measuring neural synchrony by message passing. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2007, Vancouver, Canada, December 6-9, 2007 (2008)
Kasabov, N.: EEvolving connectionist systems: The knowledge engineering approach. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Mallat, S.G., Zhang, Z.: Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 12, 3397–3415 (1993)
Press, W.H., Flannery, B.P., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T.: Numerical recipes in C: The art of scientific computing, pp. 425–430. Cambridge University Press, New York (2002)
Dubois, R., Maison-Blanche, P., Quenet, B., Dreyfus, G.: Automatic ecg wave extraction in long-term recordings using gaussian mesa function models and nonlinear probability estimators. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 88(3), 217–233 (2007)
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A.: Sparse bump sonification: a new tool for multichannel eeg diagnosis of mental disorders; application to the detection of the early stage of alzheimer’s disease. In: King, I., Wang, J., Chan, L.-W., Wang, D. (eds.) ICONIP 2006. LNCS, vol. 4234, pp. 92–101. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Dreyfus, G., Musha, T., Rutkowski, T., Gervais, R.: Blind source separation and sparse bump modelling of time frequency representation of eeg signals: New tools for early detection of alzheimer’s disease. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing 2005 (MLSP 2005), Mystic CT, USA, September 28-30 (2005)
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Dreyfus, G., Musha, T., Shishkin, S.L., Gervais, R.: Early detection of alzheimer’s disease by blind source separation, time frequency representation, and bump modeling of eeg signals (invited presentation). In: Duch, W., Kacprzyk, J., Oja, E., Zadrożny, S. (eds.) ICANN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3696, pp. 683–692. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Vialatte, F., Dauwels, J., Rutkowski, T.M., Cichocki, A.: Oscillatory event synchrony during steady state visual evoked potentials. In: Springer (ed.) Advances in Cognitive Neurodynamics, Proceedings of the First International Conference on Cognitive Neurodynamics (ICCN 2007), Shanghai, China, November 17-21, 2007 (2008)
Vialatte, F., Martin, C., Dubois, R., Haddad, J., Quenet, B., Gervais, R.: A machine learning approach to the analysis of time-frequency maps, and its application to neural dynamics. Neural Networks 20, 194–209 (2007)
Vialatte, F., Martin, C., Ravel, N., Quenet, B., Dreyfus, G., Gervais, R.: Oscillatory activity, behaviour and memory, new approaches for lfp signal analysis. In: Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis 2003. Proceedings of the 35th annual general meeting of the European Brain and Behaviour Neuroscience Society (EBBS 2003), Barcelona, Spain, September 17-20, vol. 63 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vialatte, FB., Dauwels, J., Solé-Casals, J., Maurice, M., Cichocki, A. (2009). Improved Sparse Bump Modeling for Electrophysiological Data. In: Köppen, M., Kasabov, N., Coghill, G. (eds) Advances in Neuro-Information Processing. ICONIP 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5506. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02490-0_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02490-0_28
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02489-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02490-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)