Abstract
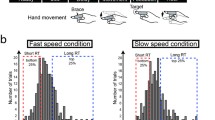
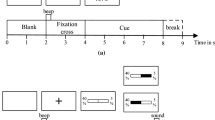
The present study aimed to investigate this tripartite relationship, regarding MRCP as a physiological index, ballistic movement as an index of operation and accuracy of the task performance. Experiments were conducted ’reaching’ task; the subject touches the target appears 300 pixels away from the start point in a vertical direction on the touch sensitive screen with the forefinger. During experiments, EEG, EMG as trigger, image by high-speed camera and the efficiency of task were acquired. As a result, significant differences between the high and poor performance groups were clear on the NS in MRCP acquired from Fz(p < 0.05), Cz (p < 0.05) and Pz (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the difference was confirmed on the duration of ballistic movement. Based on our findings, we attempted to extract MRCP rapidly and automatically without using signal averaging and discuss whether it is possible to estimate accuracy just before the motion is executed.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
References
Kornhuber, H.H., Deecke, L.: Hirnpotentialanderungen bei Willkurbewegungen und passiven Bewegungen des Menschen. Bereitschafts potential und reaffernte potentiale. Pfligers Arch, Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere 284, 1–17 (1965)
Barrett, G., Shibasaki, H., Neshige, R.A.: Computer-assisted method for averaging movement-related cortical potentials with respect to EMG onset. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 60(3), 276–281 (1985)
Shibasaki, H., Hallett, M.: What is the Bereitschaftspotential? Clin. Neurophysiol 117(11), 2341–2356 (2006)
MacKay, D.M., MacKay, V.: Behind the eye. Basil Blackwell, Malden (1991)
Yamamoto, J., Ikeda, A., Satow, T., et al.: Human eye fields in the frontal lobe as studied by epicortical recording of movement-related cortical potentials. Brain 127, 873–887 (2004)
Barrett, G., et al.: Cortical potential shifts preceding voluntary movements are nomal in parkinsonism. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 63, 340–348 (1986)
Card, S.K., Moran, T.P., Newell, A.: The psychology of human-computer interaction. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey (1983)
Gopher, D., Sanders, A.F.: S-Oh-R: Oh Stages! Oh Resources! In: Prinz, W., Sanders, A.F. (eds.) Cognition and motor processes, Springer, Heidelberg (1984)
Revelle, W.: Indivisual differences in personality and motivation: ’non-cognitive’ determinants of cognitive performance. In: Baddeley, A., Weiskrantz, L. (eds.) Awareness Control, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1991)
Flash, T., Hogan, N.: The Coordination of Arm Movements: An Experimentally Confirmed Mathematical Model. Journal of Neuroscience 5, 1688–1703 (1985)
Uno, Y., Kawato, M., Suzuki, R.: Formation and control of optimal trajectory in human multijoint arm movement - Minimum torque-change model. Biological Cybernetics 61(2), 89–101 (1989)
Kawato, M.: Optimization and learning in neural networks for formation and control of coordinated movement. In: Meyer, D., Kornblum, S. (eds.) Attention and performance XIV, pp. 821–849. MIT Press, Cambridge (1993)
Fitts, P.M., Peterson, J.R.: Information capacity of discrete motor responses. Journal of Experimental Psychology 67, 103–112 (1964)
Accot, J., Zhai, S.: Beyond Fitts’ Law: Models for trajectory-based HCI tasks. In: CHI 1997, pp. 295–302 (1997)
Flowers, K.: Ballistic and corrective movement on an aiming task. Neurology 25, 413–421 (1975)
Pratt, J., Abrams, R.A.: Practice and component submovements: The roles of programming and feedback in rapid aimed limb movements. Journal of Motor Behavior 28(2), 149–156 (1996)
Oldfield, R.C.: The assessent and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 9, 97–113 (1971)
Harris, C.M., Wolpert, D.M.: Signal-dependent noise determinations motor planning. Nature 394, 780–784 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Suzuki, S. et al. (2009). On the Possibility about Performance Estimation Just before Beginning a Voluntary Motion Using Movement Related Cortical Potential. In: Jacko, J.A. (eds) Human-Computer Interaction. New Trends. HCI 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5610. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02574-7_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02574-7_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02573-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02574-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)