Abstract
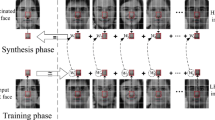
Face hallucination is to reconstruct a high-resolution face image from a low-resolution one based on a set of high- and low-resolution training image pairs. This paper proposes an example-based two-step face hallucination method through coefficient learning. Firstly, the low-resolution input image and the low-resolution training images are interpolated to the same high-resolution space. Minimizing the square distance between the interpolated low-resolution input and the linear combination of the interpolated training images, the optimal coefficients of the interpolated training images are estimated. Then replacing the interpolated training images with the corresponding high-resolution training images in the linear combination formula, the result of first step is obtained. Furthermore, a local residue compensation scheme based on position is proposed to better recover high frequency information of face. Experiments demonstrate that our method can synthesize distinct high-resolution faces.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, S., Kanade, T.: Hallucinating Faces. In: IEEE Inter. Conf. on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 83–88. IEEE Press, France (2000)
Liu, C., Shum, H.Y., Zhang, C.S.: A two-step approach to hallucinating faces: global parametric model and local nonparametric model. In: Inter. Conference on Image and Graphics, pp. 192–198. IEEE Press, New York (2001)
Chang, H., Yeung, D.-Y., Xiong, Y.: Super-resolution through neighbor embedding. In: Inter. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1275–1282. IEEE Press, Washington (2004)
Costa, G.H., Bermudez, J.C.M.: Statistical analysis of the LMS algorithm applied to super-resolution image reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 11, 2084–2095 (2007)
Zhuang, Y., Zhang, J., wu, F.: Hallucinating faces: LPH super-resolution and neighbor reconstruction for residue compensation. Pattern Recognition 40, 3178–3194 (2007)
Wang, X., Tang, X.: Hallucinating Face by Eigentransformation. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics 35, 425–434 (2005)
Gao, W., et al.: The CAS-PEAL Large-Scale Chinese Face Database and Baseline Evaluations. IEEE Transactions on System Man, and Cybernetics (Part A) 38, 149–161 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ma, X., Zhang, J., Qi, C. (2009). An Example-Based Two-Step Face Hallucination Method through Coefficient Learning. In: Kamel, M., Campilho, A. (eds) Image Analysis and Recognition. ICIAR 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5627. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02611-9_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02611-9_47
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02610-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02611-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)