Abstract
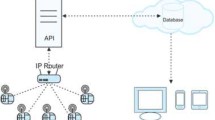
The real-time system uses a back-propagation network (BPN) with associative memory for recognition and classification in multi-sensors data fusion. This study attempts to apply classification fusion technology to the real-time signals recognition of multi-sensors data in a wireless sensor networks (WSNs) system with a node–sink mobile network structure. These wireless sensor network systems include temperature, humidity, ultraviolet, and illumination four variable measurements for environment monitoring services (EMS). Remote engineers can manage the multi-sensors data fusion using the browser, and the WSNs system then classification the data fusion database via the Internet and mobile network. Moreover, the data fields of each sensor node contain the properties and specifications of that pattern, except in the case of engineering components. The database system approach significantly improves classification data fusion system capacity. The classification fusion system examined here employs parallel computing, which increases system data fusion rate. The classification fusion system used in this work is an Internet based node–sink mobile network structure. The final phase of the classification fusion system applies database BPN technology to processing data fusion, and can solve the problem of spurious states. The system considered here is implemented on the Yang-Fen Automation Electrical Engineering Company as a case study. The experiment is continued for 4 weeks, and engineers are also used to operating the web-based classification fusion system. Therefore, the cooperative plan described above is analyzed and discussed here. Finally, these papers propose the tradition methods compare with the innovative methods.
This work was supported in part by the National Science Council Taiwan, through it’s grand no. NSC- 97-2218-E-167-001.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, F., et al.: Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. Journal of Computer Networks 38(4), 393–422 (2002)
Franceschini, F.: A review of localization algorithms for distributed wireless sensor networks in manufacturing. Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing (June 13, 2007)
Aquino, A.L.L., Figueiredo, C.M.S., Nakamura, E.F., Buriol, L., Loureiro, A.A.F., Fernandes, A.O., Coelho, C.J.N.: Data streambased algorithms for wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE AINA 2007, Niagara Falls, Canada, pp. 869–876 (2007)
Brouwer, R.K.: An integer recurrent artificial neural network for classifying feature vectors. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 14(3), 335–339 (2000)
Brouwer, R.K.: A fuzzy recurrent artificial neural network for pattern classification. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems 8(5), 525–538 (2000)
Hu, H., Lin, X., Wu, M.-Y.: Multi-Source Data Fusion and Management for Virtual Wind Tunnels and Physical Wind Tunnels. Autonomous Systems – Self-Organization, Management, and Control, 63–70 (2008)
Loskiewicz-Buczak, A., Uhrig, R.E.: Aggregation of evidence by fuzzy set operations for vibrationmonitoring. In: Third International Conference on Industrial Fuzzy Control and Intelligent Systems, IFIS apos 1993, December 1993, vol. 1(3), pp. 204–209 (1993)
Sharples, S., Callaghan, V., Clarke, G.: A multi-agent architecture for intelligent building sensing and control. International Sensor Review Journal (1999)
Varshney, P.K.: Distributed Detection and Data Fusion. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Varshney, P.K., Mohan, C.K.: On Sensor Networking and Signal Processing for Smart and Safe Buildings. In: Szymanski, B.K., Yener, B. (eds.) Advances in Pervasive Computing and Networking, pp. 213–226 (2005)
Qi, H.R., Iyengar, S.S., Chakrabarty, K.: Multiresolution data integration using mobile agents in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews 31(3), 383–391 (2001)
Kumar, R., Wolenetz, M., Agarwalla, B., Shin, J., Hutto, P., Paul, A., Ramachandran, U.: DFuse: A framework for distributed data fusion. In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, pp. 114–125. ACM Press, Los Angeles (2003)
Zhao, F., Liu, J., Liu, J.J., Guibas, L., Reich, J.: Collaborative signal and information processing: An information directed approach. Proceedings of the IEEE 91(8), 1199–1209 (2003)
Jayasimha, D.N., Iyengar, S.S., Kashyap, R.L.: Information integration and synchronization in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 21(5), 1032–1043 (1991)
Polikar, R., Udpa, L., Udpa, S.S., Taylor, T.: Frequency Invariant Classification of Ultrasonic Weld Inspection Signals. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control 45(3), 614–625 (1998)
Polikar, R., Udpa, L., Udpa, S.S., Spanner, J.: Time Scaling and Frequency Invariant Multiresolution Analysis of Ultrasonic NDE Signals. In: Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E. (eds.) Review of Progress in Quantitative NDE, vol. 17, pp. 743–749. Plenum Press, New York (1998)
Bae, S., Udpa, L., Udpa, S.S., Taylor, T.: Classification of Ultrasonic Weld Inspection Data Using Prinicipal Comoponen Analysis. In: Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E. (eds.) Review of Progress in Quantitative NDE, vol. 16, pp. 741–748. Plenum Press, New York (1997)
Ye, Y.C.: Application and Implementation on Neural Network Models. Scholars Books Co., Ltd. (2004)
Tsistsiklis, J.N.: Decentralized detection. In: Poor, H.V., Thomas, J.B. (eds.) Advances in Statistical Signal Processing, Signal Detection, vol. 2. JAI, Greenwich (1993)
Tang, Z.B., Pattipati, K.R., Kleinman, D.L.: Optimization of distributed detection networks: Part II generalized tree structures. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man Cybern. 23, 211–221 (1993)
Pados, D.A., Halford, K.W., Kazakos, D., Papantoni-Kazakos, P.: Distributed binary hypothesis testing with feedback. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man and Cybern. 25, 21–42 (1995)
Alhakeem, S., Varshney, P.K.: Decentralized ayesian hypothesis testing with feedback. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man Cybern. 26, 503–513 (1996)
Swaszek, P.F., Willett, P.: Parley as an approach to distributed detection. IEEE Trans. Aerospace Elect. Syst. 31, 447–457 (1995)
Sung, W.-T., Chung, H.-Y.: Design an Innovative Localization Engines into WSN via ZigBee and SOC. In: 2008 CACS International Automatic Control Conference (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sung, WT. (2009). Employed BPN to Multi-sensors Data Fusion for Environment Monitoring Services. In: González Nieto, J., Reif, W., Wang, G., Indulska, J. (eds) Autonomic and Trusted Computing. ATC 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5586. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02704-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02704-8_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02703-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02704-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)