Abstract
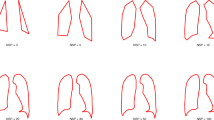
This paper presents an approach for mining 2D shape of human lungs from large x-ray image archives of a national level. Images were accumulated in framework of a compulsory computerized country-wide screening programme launched few years ago which is being under development. Three study groups of images containing about 21, 18 and 39 thousand of subjects were created by sub-sampling from a test database resulted from pulmonary x-ray examinations of a total of 188 thousands people. These groups have been well balanced by age and gender according to the existing biomedical standards and subsequently used as input data for searching different kinds of regularities in 2D projective lung shape and size. The approach followed in the paper combines different methods including procrustes shape analysis, Bookstein’s baseline shape registration, multi-dimensional scaling, regression models with broken-line relationships as well as various conventional statistical procedures. As a result, interesting gender- and age-related regularities in lung shape were discovered and documented in the paper.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsu, W., Lee, M., Zhang, J.: Image mining: Trends and developments. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems 19(1), 7–23 (2002)
Malik, H.H.: Efficient Algorithms for Clustering and Classifying High Dimensional Text and Discretized Data using Interesting Patterns. PhD Thesis, School of Arts and Sciences, Columbia University, 176 p. (2008)
Perner, P.: Image mining: Issues, framework, a generic tool and its application to medical-image diagnosis. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 15(2), 205–216 (2002)
Perner, P., Perner, H., Müller, B.: Mining knowledge for HEp-2 cell image classification. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 26(1-2), 161–173 (2002)
Gados, D., Horvath, G.: Using heuristics for the lung fields segmentation in chest radiographs. IFMBE Proceedings 16(2), 802–805 (2007)
Chen, S., Cao, L., Liu, J., Tang, X.: Automatic segmentation of lung fields from radiographic images of sars patients using a new graph cuts algorithm. In: Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2006, Hong Kong, vol. 1, pp. 271–274. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2006)
Ginneken, B., Romeny, B.: Automatic segmentation of lung fields in chest radiographs. Medical Physics 27, 2445–2455 (2000)
Dryden, I., Mardia, K.: Statistical Shape Analysis, 1st edn., 376 p. John Wiley & Sons, New York (1998)
R Development Core Team: R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (2008) ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Bookstein, F.: Size and shape spaces for landmark data in two dimensions (with discussion). Statistical Science 1, 181–242 (1986)
Muggeo, V.: Estimating regression models with unknown break-points. Statistics in Medicine 22, 3055–3071 (2003)
Cox, T., Cox, M.: Multidimensional scaling, 2nd edn., 328 p. Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton (2000)
Kovalev, V.A., Kruggel, F., von Cramon, D.Y.: Gender and age effects in structural brain asymmetry as measured by MRI texture analysis. NeuroImage 19, 895–905 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kovalev, V., Prus, A., Vankevich, P. (2009). Mining Lung Shape from X-Ray Images. In: Perner, P. (eds) Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. MLDM 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 5632. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03070-3_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03070-3_42
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03069-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03070-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)