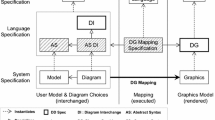
Abstract
In this paper we compare three visual notations for modelling processes, and we propose a textual notation for modelling these processes. Our textual notation can be used just as a modelling notation, but it can also be used to translate the process models from one visual notation to another.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolverine Software, http://www.wolverinesoftware.com (last accessed, 2009)
Badica, C., Badica, A., Litoiu, V.: Role activity diagrams as finite state processes. In: Proceedings of Second International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Computing, pp. 15–22 (2003)
Dumas, M., Ter Hofstede, A.: UML activity diagrams as a workflow specification language. LNCS, pp. 76–90. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Holt, A., Ramsey, H., Grimes, J.: Coordination system technology as the basis for a programming environment. Electrical Communication 57(4), 307–314 (1983)
Notation, B.: 1.1 Specification. Tech. rep., Technical report, OMG, 2008 (2008)
Odeh, M., Kamm, R.: Bridging the gap between business models and system models. Information and Software Technology 45(15), 1053–1060 (2003)
Ould, M.: Business Processes: Modelling and Analysis for Re-engineering and Improvement. John Wiley and Sons, West Sussex (1995)
Phalp, K., Henderson, P., Walters, R., Abeysinghe, G.: RolEnact: role-based enactable models of business processes. Information and Software Technology 40(3), 123–133 (1998)
Specification, O.: Version 1.4, September 2001. Object Management Group, Inc., Framingham, Mass (2001), Internet: http://www.omg.org
Urzica, A., Tanase, C.: Mapping BPMN to AUML: Towards an automatic process. In: Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science, pp. 539–547 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mogos, AH., Urzica, A. (2009). TN4PM: A Textual Notation for Process Modelling. In: Papadopoulos, G.A., Badica, C. (eds) Intelligent Distributed Computing III. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 237. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03214-1_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03214-1_29
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03213-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03214-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)