Abstract
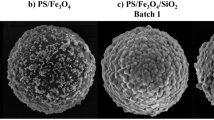
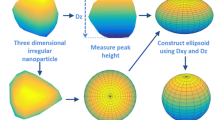
In nano-medicine, mesoporous silicon particles provide efficient vehicles for the dissemination and delivery of key proteins at the micron scale. We propose a new quality-control method for the nanopore structure of these particles, based on image analysis software developed to automatically inspect scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) images of nanoparticles in a fully automated fashion. Our algorithm first identifies the precise position and shape of each nanopore, then generates a graphic display of these nanopores and of their boundaries. This is essentially a texture segmentation task, and a key quality-control requirement is fast computing speed. Our software then computes key shape characteristics of individual nanopores, such as area, outer diameter, eccentricity, etc., and then generates means, standard deviations, and histograms of each pore-shape feature. Thus, the image analysis algorithms automatically produce a vector from each image which contains relevant nanoparticle quality control characteristics, either for comparison to pre-established acceptability thresholds, or for the analysis of homogeneity and the detection of outliers among families of nanoparticles.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canham, L.: Bioactive silicon structure fabrication through nanoetching techniques. Adv. Mater. 7, 1033–1037 (1995)
Cheng, M., et al.: Nanotechnologies for biomolecular detection and medical diagnostics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 10, 11–19 (2006)
Bayliss, S., et al.: Nature of the silicon-animal cell interface. J. Porus Mater 7, 191–195 (2000)
Li, Y., et al.: Polymer replicas of photonic porous silicon for sensing and drug delivery applications. Science 299, 2045–2047 (2003)
Buckberry, L., Bayliss, S.: Porous silicon as a biomaterial. Mater World 7, 213–215 (1999)
Sun, W., Puzas, J., Sheu, T.J., Fauchet, P.: Porous silicon as a cell interface for bone tissue engineering. Phys. Status Solidi A 204, 1429–1433 (2007)
Salonena, J., et al.: Mesoporous silicon microparticles for oral drug delivery: Loading and release of five model drugs. J. Controlled Release 108, 362–374 (2005)
Prestidge, C., et al.: Peptide and protein loading into porous silicon wafers. Phys. Status Solidi C 205, 311–315 (2008)
Canham, L.: Nanoscale semiconducting silicon as a nutritional food additive. Nanotechnol. 18, 185704 (2007)
Foraker, A., et al.: Microfabricated porous silicon particles enhance paracellular delivery of insulin across intestinal caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm. Res. 20, 110–116 (2003)
Decuzzi, P., Lee, S., Bhushan, B., Ferrari, M.: A theoretical model for the margination of particles within blood vessels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33, 179–190 (2005)
Decuzzi, P., Ferrari, M.: Design maps for nanoparticles targeting the diseased microvasculature. Biomaterials 29, 377–384 (2008)
Gentile, F., Ferrari, M., Decuzzi, P.: The transport of nanoparticles in blood vessels: The effect of vessel permeability and blood rheology. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 36, 254–261 (2008)
Serda, R., et al.: Porous silicon particles for imaging and therapy of cancer. In: Kumar, C.S. (ed.) Nanomaterials for the Life Sciences. Nanostructured Oxides of Nanomaterials for the Life Sciences, vol. 2, p. 359. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2009)
Martin, F., et al.: Acute toxicity of intravenously administered microfabricated silicon dioxide drug delivery particles in mice: Preliminary findings. Drugs R D 6, 71 (2005)
Tasciotti, E., et al.: Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nature 3, 151–157 (2008)
Gentile, F., et al.: The effect of shape on the margination dynamics of non-neutrally buoyant particles in two-dimensional shear flows. J. Biomech. (2008)
Bouaynaya, N., Schonfeld, D.: Theoretical foundations of spatially-variant mathematical morphology part II: Gray-level images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Machine Intelligence 30, 837–850 (2008)
Soille, P.: Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alexander, S.K. et al. (2009). SEM Image Analysis for Quality Control of Nanoparticles. In: Jiang, X., Petkov, N. (eds) Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. CAIP 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5702. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03767-2_72
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03767-2_72
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03766-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03767-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)