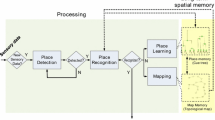
Abstract
Topological maps are graph-based representations of space and have been considered as an alternative to metric representations in the context of robot navigation. In this work, we seek to improve on the lack of robustness of current topological mapping systems against ambiguity in the available information about the environment. For this purpose, we develop a topological mapping system that tracks multiple graph hypotheses simultaneously. The feasibility of the overall approach depends on a reduction of the search space by exploiting spatial constraints. We here consider qualitative direction information and the assumption that the map has to be planar. Qualitative spatial reasoning techniques are used to check the satisfiability of individual hypotheses. We evaluate the effects of absolute and relative direction information using relations from two different qualitative spatial calculi and combine the approach with a topological mapping system based on Voronoi graphs realized on a real robot.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thrun, S.: Robotic mapping: A survey. In: Lakemeyer, G., Nebel, B. (eds.) Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millenium. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (2002)
Kuipers, B.: The Spatial Semantic Hierarchy. Artificial Intelligence (119), 191–233 (2000)
Remolina, E., Kuipers, B.: Towards a general theory of topological maps. Artificial Intelligence 152(1), 47–104 (2004)
Werner, S., Krieg-Brückner, B., Herrmann, T.: Modelling navigational knowledge by route graphs. In: Habel, C., Brauer, W., Freksa, C., Wender, K.F. (eds.) Spatial Cognition 2000. LNCS, vol. 1849, pp. 295–316. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Dudek, G., Jenkin, M., Milios, E., Wilkes, D.: Robotic exploration as graph construction. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation 7(6), 859–865 (1991)
Dudek, G., Freedman, P., Hadjres, S.: Using multiple models for environmental mapping. Journal of Robotic Systems 13(8), 539–559 (1996)
Kuipers, B., Modayil, J., Beeson, P., MacMahon, M., Savelli, F.: Local metrical and global topological maps in the hybrid Spatial Semantic Hierarchy. In: Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2004 (ICRA 2004), pp. 4845–4851 (2004)
Moratz, R., Nebel, B., Freksa, C.: Qualitative spatial reasoning about relative position: The tradeoff between strong formal properties and successful reasoning about route graphs. In: Freksa, C., Brauer, W., Habel, C., Wender, K.F. (eds.) Spatial Cognition III. LNCS, vol. 2685, pp. 385–400. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Moratz, R., Wallgrün, J.O.: Spatial reasoning about relative orientation and distance for robot exploration. In: Kuhn, W., Worboys, M.F., Timpf, S. (eds.) COSIT 2003. LNCS, vol. 2825, pp. 61–74. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Savelli, F., Kuipers, B.: Loop-closing and planarity in topological map-building. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2004), pp. 1511–1517 (2004)
Ligozat, G.: Reasoning about cardinal directions. Journal of Visual Languages and Computing 9, 23–44 (1998)
Moratz, R.: Representing relative direction as binary relation of oriented points. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2006), August 2006, pp. 407–411 (2006)
Wallgrün, J.O.: Autonomous construction of hierarchical voronoi-based route graph representations. In: Freksa, C., Knauff, M., Krieg-Brückner, B., Nebel, B., Barkowsky, T. (eds.) Spatial Cognition IV. LNCS, vol. 3343, pp. 413–433. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cohn, A.G., Hazarika, S.M.: Qualitative spatial representation and reasoning: An overview. Fundamenta Informaticae 46(1-2), 1–29 (2001)
Hopcroft, J., Tarjan, R.: Efficient planarity testing. Journal of the ACM 21(4), 549–568 (1974)
Wallgrün, J.O., Frommberger, L., Wolter, D., Dylla, F., Freksa, C.: Qualitative spatial representation and reasoning in the sparQ-toolbox. In: Barkowsky, T., Knauff, M., Ligozat, G., Montello, D.R. (eds.) Spatial Cognition 2007. LNCS, vol. 4387, pp. 39–58. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Mackworth, A.: Consistency in networks of relations. Artificial Intelligence 8(1), 99–118 (1977)
Montanari, U.: Networks of constraints: Fundamental properties and applications to picture processing. Information Science 7(2), 95–132 (1974)
Choset, H., Walker, S., Eiamsa-Ard, K., Burdick, J.: Sensor-based exploration: Incremental construction of the Hierarchical Generalized Voronoi Graph. The International Journal of Robotics Research 19(2), 126–148 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wallgrün, J.O. (2009). Exploiting Qualitative Spatial Constraints for Multi-hypothesis Topological Map Learning. In: Hornsby, K.S., Claramunt, C., Denis, M., Ligozat, G. (eds) Spatial Information Theory. COSIT 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5756. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03832-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03832-7_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-03831-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-03832-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)