Abstract
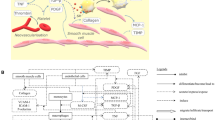
Atherosclerosis, a pathology affecting arterial blood vessels, is one of most common diseases of the developed countries. We present studies on the increased atherosclerosis risk using an agent based model of atherogenesis that has been previously validated using clinical data. It is well known that the major risk in atherosclerosis is the persistent high level of low density lipoprotein (LDL) concentration. However, it is not known if short period of high LDL concentration can cause irreversible damage and if reduction of the LDL concentration (either by life style or drug) can drastically or partially reduce the already acquired risk. We simulated four different clinical situations in a large set of virtual patients (200 per clinical scenario). In the first one the patients lifestyle maintains the concentration of LDL in a no risk range. This is the control case simulation. The second case is represented by patients having high level of LDL with a delay to apply appropriate treatments; The third scenario is characterized by patients with high LDL levels treated with specific drugs like statins. Finally we simulated patients that are characterized by several oxidative events (smoke, sedentary life style, assumption of alcoholic drinks and so on so forth) that effective increase the risk of LDL oxidation. Those preliminary results obviously need to be clinically investigated. It is clear, however, that SimAthero has the power to concretely help medical doctors and clinicians in choosing personalized treatments for the prevention of the atherosclerosis damages.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A.K., Lichtman, A.H., Pillai, S.: Cellular and molecular immunology, 6th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia (2007)
Artieda, M., Cenarro, A., Gañàn, A., Jericó, I., Gonzalvo, C., Casado, J.M., Vitoria, I., Puzo, J., Pocoví, M., Civeira, F.: Serum chitotriosidase activity is increased in subjects with atherosclerosis disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 1645–1652 (2003)
Artieda, M., Cenarro, A., Gańàn, A., Lukic, A., Moreno, E., Puzo, J., Pocoví, M., Civeira, F.: Serum chitotriosidase activity, a marker of activated macrophages, predicts new cardiovascular events independently of C-Reactive Protein. Cardiology 108, 297–306 (2007)
Berliner, J.A., Heinecke, J.W.: The role of oxidized lipoproteins in atherogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 20(5), 707–727 (1999)
Brizzi, P., Isaja, T., D’Agata, A., Malaguarnera, A., Malaguarnera, M., Musumeci, S.: Oxidized LDL antibodies (OLAB) in patients with beta-thalassemia major. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 9(3), 139–144 (2002)
Brizzi, P., Tonolo, G., Carusillo, F., Malaguarnera, M., Maioli, M., Musumeci, S.: Plasma Lipid Composition and LDL Oxidation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 41(1), 56–60 (2003)
Brizzi, P., Tonolo, G., Bertrand, G., Carusillo, F., Severino, C., Maioli, M., Malaguarnera, L., Musumeci, S.: Autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) and LDL oxidation status. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 42(2), 164–170 (2004)
Hanson, G.K.: Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352(16), 1685–1695 (2005)
Klimov, A.N., Nikul’cheva, N.G.: Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism and Its Disturbances. Piter Kom, St. Petersburg (1999)
Law, M.R., Wald, N.J., Rudnicka, A.R.: Quantifying effect of statins on low density lipoprotein cholesterol, ischaemic heart disease, and stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 326(7404), 1423 (2003)
Orem, C., Orem, A., Uydu, H.A., Celik, S., Erdol, C., Kural, B.V.: The effects of lipid-lowering therapy on low-density lipoprotein auto-antibodies: relationship with low-density lipoprotein oxidation and plasma total antioxidant status. Coron. Artery Dis. 13(1), 56–71 (2002)
Pappalardo, F., Musumeci, S., Motta, S.: Modeling immune system control of atherogenesis. Bioinformatics, 24(15), 1715–1721 (2008)
Romero-Corral, A., Somers, V.K., Korinek, J., Sierra-Johnson, J., Thomas, R.J., Allison, T.G., Lopez-Jimenez, F.: Update in prevention of atherosclerotic heart disease: management of major cardiovascular risk factors. Rev. Invest. Clin. 58(3), 237–244 (2006)
Ross, R.: Atherosclerosis–an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 340(2), 115–126 (1999)
Shaw, P.X., Hörkkö, S., Tsimikas, S., Chang, M.K., Palinski, W., Silverman, G.J., Chen, P.P., Witztum, J.L.: Human-derived anti-oxidized LDL autoantibody blocks uptake of oxidized LDL by macrophages and localizes to atherosclerotic lesions in vivo.t Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21(8), 1333–1339 (2001)
Shoji, T., Nishizawa, Y., Fukumoto, M., Shimamura, K., Kimura, J., Kanda, H., Emoto, M., Kawagishi, T., Morii, H.: Inverse relationship between circulating oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and anti-oxLDL antibody levels in healthy subjects. Atherosclerosis 148(1), 171–177 (2000)
Steinberg, D.: Low density lipoprotein oxidation and its pathobiological significance. J. Biol. Chem. 272(34), 20963–20966 (1997)
Tinahones, F.J., Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M., Rojo-Martinez, G., Cardona, F., Esteva de Antonio, I.E., Ruiz de Adana, M.S., Soriguer, F.K.: Increased levels of anti-oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies are associated with reduced levels of cholesterol in the general population. Metabolism 51(4), 429–431 (2002)
Tinahones, F.J., Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M., Garrido-Sanchez, L., Garcia-Fuentes, E., Rojo-Martinez, G., Esteva, I., Ruiz de Adana, M.S., Cardona, F., Soriguer, F.: Influence of age and sex on levels of anti-oxidized LDL antibodies and anti-LDL immune complexes in the general population. J. Lipid Res. 46(3), 452–457 (2005)
Vinereanu, D.: Risk factors for atherosclerotic disease: present and future. Herz, Suppl. 3, 5–24 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pappalardo, F., Cincotti, A., Motta, A., Pennisi, M. (2009). Agent Based Modeling of Atherosclerosis: A Concrete Help in Personalized Treatments. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Lee, HH., Kang, HJ., Bevilacqua, V. (eds) Emerging Intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. With Aspects of Artificial Intelligence. ICIC 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 5755. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04020-7_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04020-7_41
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04019-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04020-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)