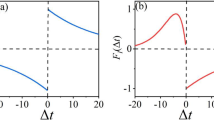
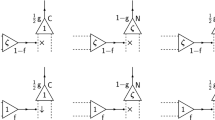
Abstract
In this study, the generation of temporal synchrony within an artificial neural network is examined considering a stochastic synaptic model. A network is introduced and driven by Poisson distributed trains of spikes along with white-Gaussian noise that is added to the internal synaptic activity representing the background activity (neuronal noise). A Hebbian-based learning rule for the update of synaptic parameters is introduced. Only arbitrarily selected synapses are allowed to learn, i.e. change parameter values. The average of the cross-correlation coefficients between a smoothed version of the responses of all the neurons is taken as an indicator for synchrony. Results show that a network using such a framework is able to achieve different states of synchrony via learning. Thus, the plausibility of using stochastic-based models in modeling the neural process is supported. It is also consistent with arguments claiming that synchrony is a part of the memory-recall process and copes with the accepted framework in biological neural systems.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsodyks, M., Uziel, A., Markram, H.: Synchrony generation in recurrent networks with frequency-dependent synapses. J. Neurosci. 20, 50 (2000)
König, P., Engel, A.K., Roelfsema, P.R., Singer, W.: How precise is neuronal synchronization? Neural Comput. 7(3), 469–485 (1995)
Hansel, D., Mato, G., Meunier, C.: Synchrony in excitatory neural networks. Neural Comput. 7(2), 307–337 (1995)
Sejnowski, T.J., Paulsen, O.: Network Oscillations: Emerging Computational Principles. J. Neurosci. 26(6), 1673–1676 (2006)
Fellous, J.M., Rudolph, A.M., Destexhe, B.A., Sejnowski, T.J.: Synaptic background noise controls the input/output characteristics of single cells in an in vitro model of in vivo activity. Neuroscience 122, 811–829 (2003)
Lindner, B., Schimansky-Geier, L., Longtin, A.: Maximizing spike train coherence or incoherence in the leaky integrate-and-fire model. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 66(3 pt. 1), 031916 (2002)
Kreuz, T., Haas, J., Morelli, A., Abarbanel, H.D., Politi, A.: Measuring spike train synchrony and reliability. BMC Neuroscience 8(suppl. 2), 79 (2007)
Durstewitz, D.: Self-Organizing Neural Integrator Predicts Interval Times through Climbing Activity. J. Neurosci. 4(12) (2003)
Singer, W.: Neuronal synchrony: a versatile code for the definition of relations. Neuron 24, 49–65 (1999)
Gray, C.M.: The temporal correlation hypothesis of visual feature integration: Still alive and well. Neuron 24(1), 31–47 (1999)
Salinas, E., Sejnowski, T.J.: Correlated neuronal activity and the flow of neural information. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2, 539–550 (2001)
von der Malsburg, C.: The what and why of binding: The modeler’s perspective (1999)
Singer, W., Gray, C.M.: Visual feature integration and the temporal correlation hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 555–586 (1995)
Averbeck, B.B., Latham, P.E., Pouget, A.: Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 7, 358–366 (2006)
Campbell, S.R., Wang, D.L., Jayaprakash, C.: Synchrony and desynchrony in integrate-and-fire oscillators. Neural Computation 11(7), 1595–1619 (1999)
Neltner, L., Hansel, D.: On synchrony of weakly coupled neurons at low firing rate. Neural Comput. 13(4), 765–774 (2001)
Bressloff, P.C., Coombes, P.S.: Dynamics of strongly coupled spiking neurons. Neural Comput. 12(1), 91–129 (2000)
Vreeswijk, C.V., Hansel, D.: Patterns of synchrony in neural networks with spike adaptation. Neural Comput. 13(5), 959–992 (2001)
Mikula, S., Niebur, E.: Rate and synchrony in feedforward networks of coincidence detectors: Analytical solution. Neural Comput. 17(4), 881–902 (2005)
DeVille, R.E.L., Peskin, C.S.: Synchrony and Asynchrony in a Fully Stochastic Neural Network. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology 70(6), 1608–1633 (2008)
Holcman, D., Tsodyks, M.: The Emergence of Up and Down States in Cortical Networks. Science 2(3), 174–181 (2006)
Maass, W., Zador, A.M.: Dynamic stochastic synapses as computational units. Neural Computation 11, 903–917 (1999)
Natschlager, T.: Efficient Computation in Networks of Spiking Neurons Simulations and Theory. PhD thesis, Institute of Theoretical Computer Science, Austria (1999)
Natschlager, T., Maass, W., Zador, A.: Efficient temporal processing with biologically realistic dynamic synapses. Computation in neural system 12, 75–78 (2001)
Kroger, H.: Why are probabilistic laws governing quantum mechanics and neurobiology? Solitons and Fractals 25, 815 (2005)
Namarvar, H.H., Liaw, J.S., Berger, T.W.: A new dynamic synapse neural network for speech recognition. IEEE Trans., 2985–2990 (2001)
Liaw, J.S., Berger, T.W.: Dynamic synapse: A new concept of neural representation and computation. Hippocampus 6, 591–600 (1996)
Herzog, M.H., Esfeld, M., Gerstner, W.: Consciousness & the small network argument. Neural Networks 20(9), 1054 (2007); Brain and Consciousness
Dodla, R., Wilson, C.: Synchrony-asynchrony transitions in neuronal networks. BMC Neuroscience 9(suppl. 1), 9 (2008)
Schreiber, S., Fellous, J.M., Whitmer, D., Tiesinga, P., Sejnowski, T.J.: A new correlation-based measure of spike timing reliability. Neurocomputing (52-54), 925–931 (2003)
Liaw, J.S., Berger, T.W.: Computing with dynamic synapses: A case study of speech recognition. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Networks, pp. 352–355 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
El-Laithy, K., Bogdan, M. (2009). Synchrony State Generation in Artificial Neural Networks with Stochastic Synapses. In: Alippi, C., Polycarpou, M., Panayiotou, C., Ellinas, G. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks – ICANN 2009. ICANN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5768. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04273-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04274-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)