Abstract
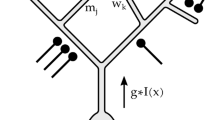
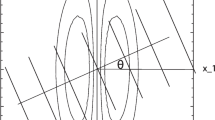
Image coding by the mammalian visual cortex has been modeled through linear combinations of receptive-field-like functions. The spatial receptive field of a visual neuron is typically assumed to be signal-independent, a view that has been challenged by recent neurophysiological findings. Motivated by these, we here propose a model for conjoint space-frequency image coding based on stimulus-dependent receptive-field-like functions. For any given frequency, the parameters of the coding functions are obtained from the Fourier transform of the stimulus. The representation is initially presented in terms of Gabor functions, but can be extended to more general forms, and we find that the resulting coding functions show properties that are consistent with those of the receptive fields of simple cortical cells of the macaque.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hubel, D.H., Wiesel, T.: Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 160, 106–154 (1962)
Marcelja, S.: Mathematical description of the responses of simple cortical cells. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 70, 1297–1300 (1980)
Olshausen, B.A., Field, D.J.: Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images. Nature 381, 607–609 (1996)
Allman, J., Miezin, F., McGuinness, E.: Stimulus specific responses from beyond the classical receptive field: Neurophysiological mechanisms for local-global comparison in visual neurons. Annu. Rev. Neuroscience 8, 407–430 (1985)
David, S.V., Vinje, W.E., Gallant, J.L.: Natural stimulus statistics alter the receptive field structure of V1 neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience 24(31), 6991–7006 (2004)
Bair, W.: Visual receptive field organization. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 15(4), 459–464 (2005)
Daugman, J.: Complete discrete 2-D Gabor transform by neural networks for image analysis and compression. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing 36(7), 1169–1179 (1988)
DeValois, R.L., Albrecht, D.G., Thorell, L.G.: Spatial frequency selectivity of cells in macaque visual cortex. Vision Res. 22, 545–559 (1987)
Ringach, D.L.: Spatial structure and symmetry of simple-cell receptive fileds in macaque primary visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 88, 455–463 (2002)
van Hateren, J.H., van der Schaaf, A.: Independent component filters of natural images compared with simple cells in primary visual cortex. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 265, 359–366 (1998)
Stork, D.G., Wilson, H.R.: Do Gabor functions provide appropriate descriptions of visual cortical receptive fields? J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 7, 1362–1373 (1990)
Hecht, E.: Optics. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Torreão, J.R.A., Fernandes, J.L., Victer, S.M.C. (2009). A Model for Neuronal Signal Representation by Stimulus-Dependent Receptive Fields. In: Alippi, C., Polycarpou, M., Panayiotou, C., Ellinas, G. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks – ICANN 2009. ICANN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5768. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_37
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04273-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04274-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)