Abstract
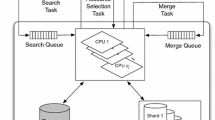
This paper presents a hybrid scavenger grid as an underlying hardware architecture for search services within digital libraries. The hybrid scavenger grid consists of both dedicated servers and dynamic resources in the form of idle workstations to handle medium- to large-scale search engine workloads. The dedicated resources are expected to have reliable and predictable behaviour. The dynamic resources are used opportunistically without any guarantees of availability. Test results confirmed that indexing performance is directly related to the size of the hybrid grid and intranet networking does not play a major role. A system-efficiency and cost-effectiveness comparison of a grid and a multiprocessor machine showed that for workloads of modest to large sizes, the grid architecture delivers better throughput per unit cost than the multiprocessor, at a system efficiency that is comparable to that of the multiprocessor.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asaduzzaman, S.: Managing Opportunistic and Dedicated Resources in a Bi-modal Service Deployment Architecture. PhD thesis. McGill University (2007)
Badue, C., Golgher, P., Barbosa, R., Ribeiro-Neto, B., Ziviani, N.: Distributed processing of conjunctive queries. In: Heterogeneous and Distributed IR workshop at the 28th ACM SIGIR Salvador,Brazil (2005)
Barroso, L.A., Dean, J., Hölzle, U.: Web search for a planet: The Google Cluster Architecture. IEEE Micro. 23(2), 22–28 (2003)
Baru, C.K., Moore, R.W., Rajasekar, A., Wan, M.: The SDSC storage resource broker. In: Proceedings of the 1998 conference of the Centre for Advanced Studies on Collaborative Research,Toronto, Canada (1998)
Baeza-Yates, R., Castillo, C., Junqueira, F., Plachouras, V., Silvestri, F.: Challenges on distributed web retrieval. In: ICDE, Istanbul, Turkey, pp. 6–20. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2007)
Computerworld Inc. Storage power costs to approach $2B this year (2009), http://www.computerworld.com
Das, S., Tewari, S., Kleinrock, L.: The case for servers in a peer-to-peer world. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications, Istanbul, Turkey (2006)
EPrints. Open access and institutional repositories with EPrints (2009), http://www.eprints.org/
FAST. FAST enterprise search (2008), http://www.fastsearch.com
FightAIDS@Home. Fight AIDS at Home (2008), http://fightaidsathome.scripps.edu/
Intel Cooporation. Intel processor pricing (2009), http://www.intc.com/priceList.cfm
Google. The Google Insights for Search (2008), http://www.google.com/insights/search/
Google. The Google search appliance (2008), http://www.google.com/enterprise/index.html
Hadoop. Apache Hadoop (2008), http://hadoop.apache.org/
Litzkow, M., Livny, M.: Experience with the condor distributed batch system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Experimental Distributed Systems (1990)
Lucene. Lucence search engine (2008), http://lucene.apache.org/
Meij, E., Rijke, M.: Deploying Lucene on the grid. In: Open Source Information Retrieval Workshop at the 29th ACM Conference on Research and Development on Information Retrieval, Seattle, Washington (2006)
Michel, S., Triantafillou, P., Weikum, G.: MINERVA: a scalable efficient peer-to-peer search engine. In: Proceedings of the ACM/IFIP/USENIX 2005 International Conference on Middleware. Grenoble, Greece (2005)
OmniFind. OmniFind search engine (2008), http://www-306.ibm.com/software/data/enterprise-search/omnifind-yahoo
Pouwelse, J.A., Garbacki, P., Epema, D.H.J., Sips, H.J.: The bittorrent p2p file-sharing system: Measurements and analysis. In: Castro, M., van Renesse, R. (eds.) IPTPS 2005. LNCS, vol. 3640, pp. 205–216. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
SETI@Home. Search for extraterrestrial intelligence at home (2007), http://setiathome.berkeley.edu/
Wood, D.A., Hill, M.D.: Cost-effective parallel computing. IEEE Computer 28, 69–72 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nakashole, N., Suleman, H. (2009). A Hybrid Distributed Architecture for Indexing. In: Agosti, M., Borbinha, J., Kapidakis, S., Papatheodorou, C., Tsakonas, G. (eds) Research and Advanced Technology for Digital Libraries. ECDL 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5714. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04346-8_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04346-8_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04345-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04346-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)