Abstract
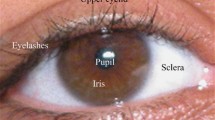
Most of the state-of-the-art iris recognition algorithms focus on processing and recognition of the ideal iris images which are captured in a controlled environment. In this paper, we process the nonideal iris images which are acquired in an unconstrained situation and are affected severely by gaze deviation, eyelids and eyelashes occlusion, non uniform intensity, motion blur, reflections, etc. To segment the nonideal iris images accurately, we deploy a variational level set based curve evolution scheme, which uses significantly larger time step for numerically solving the evolution partial differential equation (PDE), and therefore, speeds up the curve evolution process drastically. Genetic Algorithms (GAs) are deployed to select the subset of informative features by combining the valuable outcomes from the multiple feature selection criteria without compromising the recognition accuracy. The verification performance of the proposed scheme is validated using three nonideal iris datasets, namely, UBIRIS Version 2, ICE 2005, and WVU datasets.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daugman, J.: How iris recognition works. IEEE Transaction on Circuits, Systems and Video Technology 14(1), 1–17 (2003)
Daugman, J.: New methods in iris recognition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B 37(5), 1167–1175 (2007)
Schuckers, S.A.C., Schmid, N.A., Abhyankar, A., Dorairaj, V., Boyce, C.K., Hornak, L.A.: On techniques for angle compensation in nonideal iris recognition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B 37(5), 1176–1190 (2007)
Vatsa, M., Singh, R., Noore, A.: Improving iris recognition performance using segmentation, quality enhancement, match score fusion, and indexing. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B 38(4), 1021–1035 (2008)
Ross, A., Shah, S.: Segmenting non-ideal irises using geodesic active contours. In: Biometric Consortium Conference, IEEE Biometrics symposium, pp. 1–6 (2006)
Li, C., Xu, C., Gui, C., Fox, M.D.: Level set evolution without re-initialization: a new variational formulation. In: Int. Conf. on Comp. Vis. and Pattern Recog., vol. 1, pp. 430–436 (2005)
Deb, K.: Multi-objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms. J. Wiley, West Sussex (2004)
Roy, K., Bhattacharya, P.: Adaptive asymmetrical SVM and genetic algorithms based iris recognition. In: Int. Conf. on Pattern Recog., pp. 1–4 (2008)
Roy, K., Bhattacharya, P.: Level set approaches and adaptive asymmetrical SVMs applied for nonideal iris recognition. In: Kamel, M., Campilho, A. (eds.) ICIAR 2009. LNCS, vol. 5627, pp. 418–428. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Vapnik, V.N.: Statistical Learning Theory. J. Wiley, New York (1998)
Li, Q., Jiao, L., Hao, Y.: Adaptive simplification of solution for support vector machine. Pattern Recognition 40, 972–980 (2007)
Iris Challenge Evaluation (ICE) dataset found, http://iris.nist.gov/ICE/
Iris Dataset obtained from West Virginia University (WVU), http://www.wvu.edu/
UBIRIS dataset obtained from department of computer science, University of Beira Interior, Portugal, http://iris.di.ubi.pt/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Roy, K., Bhattacharya, P. (2009). Iris Recognition in Nonideal Situations. In: Samarati, P., Yung, M., Martinelli, F., Ardagna, C.A. (eds) Information Security. ISC 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5735. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04474-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04474-8_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04473-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04474-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)