Abstract
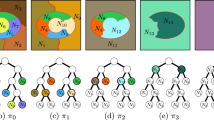
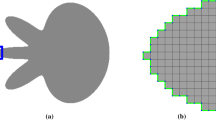
Recently, we introduced a hierarchical finite element model in the context of structural image segmentation. Such model deforms from its equilibrium shape into similar shapes under the influence of both, image–based forces and structural forces, which serve the propagation of deformations across the hierarchy levels. Such forces are very likely to result in large (rotational) deformations, which yield under the linear elasticity model artefacts and thus poor segmentation results. In this paper, we provide results indicating that different implementations of the stiffness warping method can be successfully combined to simulate dependent rotational deformations correctly, and in an efficient manner.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sclaroff, S., Pentland, A.: Modal matching for correspondence and recognition. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 17(6), 545–561 (1995)
Cootes, T., et al.: The use of active shape models for locating objects in medical images. Imag. Vis. Comp. 12(16), 355–366 (1994)
Pentland, A.: Recognition by parts. In: Proc. IEEE ICCV, pp. 612–620 (1987)
Ullman, S., Basri, R.: Recognition by linear combinations of models. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 13(10), 992–1005 (1991)
Heap, A., Hogg, D.: Improving Specificity in PDMs using a Hierarchical Approach. In: Proc. BMVC, pp. 80–89 (1997)
Al-Zubi, S., Toennies, K.D.: Extending active shape models to incorporate a-priori knowledge about structural variability. In: Van Gool, L. (ed.) DAGM 2002. LNCS, vol. 2449, p. 338. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Felzenszwalb, P., Huttenlocher, D.: Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int. J. Comp. Vis. 61(1), 55–79 (2003)
Ren, X., et al.: Recovering human body configurations using pairwise constraints between parts. In: Proc. IEEE ICCV, pp. 824–831 (2005)
Zhe, L., et al.: Hierarchical part–template matching for human detection and segmentation. In: Proc. IEEE ICCV, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Wang, Y., Mori, G.: Multiple tree models for occlusion and spatial constraints in human pose estimation. In: Proc. ECCV, pp. 710–724 (2008)
Felzenszwalb, P., et al.: A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model. In: Proc. IEEE CVPR, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Engel, K., et al.: A two–level dynamic model for the representation and recognition of cortical folding patterns. In: Proc. IEEE ICIP, pp. 297–300 (2005)
Zhu, L., Yuille, A.: A hierarchical compositional system for rapid object detection. In: Proc. NIPS (2005)
Pentland, A., Sclaroff, S.: Closed–form solutions to physically based shape modeling and recognition. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 13(7), 715–729 (1991)
Terzopoulos, D., et al.: Elastically deformable models. In: Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 205–214 (1987)
Müller, M., et al.: Stable real–time deformations. In: Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH, pp. 49–54 (2002)
Kendall, D.: A survey of the statistical theory of shape. Stat. Sci. 4, 87–120 (1989)
Tao, H., Huang, T.: Connected vibrations: a modal analysis approach to non-rigid motion tracking. In: Proc. IEEE CVPR, pp. 1424–1426 (1998)
Xu, C., Prince, J.: Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Imag. Proc. 7(3), 359–369 (1998)
Huang, J., et al.: Geometrically based potential energy for simulating deformable objects. Vis. Comput. 22(9), 740–748 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Engel, K., Toennies, K. (2009). Stable Structural Deformations. In: Fritz, M., Schiele, B., Piater, J.H. (eds) Computer Vision Systems. ICVS 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5815. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04667-4_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04667-4_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04666-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04667-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)