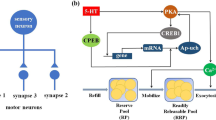
Abstract
Acting as nanobiomachines within the cell, myosin V molecular motors contribute greatly to the LTP (Long Term Potentiation) in neural signaling, which transport the recycling endosomes from the dendrite to the spine of neurons and the GluR1 in AMPA receptors lead to the activities of memorization in brains. However it is unknown that how the restriction of GluR1 at the spine of neuron is caused by the signaling cascade of myosin V and Rab11/Rab11-FIP2 during the myosin V centered signaling process in neurons. Here we report that the feedback of the biochemical reaction for binding Myosin V and Rab11/Rab11-FIP2 plays a pivotal role to restrict the accumulation of GluR1 at the spine. We have investigated the feedback of myosin V and Rab11/Rab11-FIP2 on the convergence of GluR1 by using the computational model of intracellular signaling pathway networks we designed and the simulation software Cell Illustrator Professional Version 3.0 ®. The obtained results show that controllability of molecular motor based nanobiomachines is inevitable for exploring the molecular mechanism of neuroscience at the nanoscale.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z., Edwards, J.G., Riley, N., Provance, D.W., Karcher, R., Li, X., Davison, I.G., Ikebe, M., Mercer, J.A., Kauer, J.A., Ehler, M.D.: Myosin Vb Mobilizes Recycling Endosomes and AMPA Receptors for Postsynaptic Plasticity. Cell 135, 535–548 (2008)
Goda, Y.: Along memory lane. Nature 456, 590–591 (2008)
Adachi, K., Oiwa, K., Nishizaka, T., Furuike, S., Noji, H., Itoh, H., Yoshida, M.M., Kinosita, K.: Coupling of rotation and catalysis in F1-ATPase revealed by single-molecule imaging and manipulation. Cell 130, 309–321 (2007)
Burgess, S.A., Walker, M.L., Sakakibara, H., Knight, P.J., Oiwa, K.: Dynein structure and power stroke. Nature 421, 715–718 (2003)
Oiwa, K., Kometani, R., Li, D.Y., Shitaka, Y., Nakamori, R., Matsui, S., Sakakibara, H.: Molecular and Nanometer-Scale Self-Organized System Generated by Protein Motor Functions. Materials Science Forum 539, 3290–3296 (2007)
Iwamoto, H., Oiwa, K., Kovacs, M., Sellers, J., Suzuki, T., Wakayama, J., Tamura, T., Yagi, N., Fujisawa, T.: Diversity of structural behavior in vertebrate conventional myosins complexed with actin. Journal of Molecular Biology 369, 249–264 (2007)
Noda, N., Imafuku, Y., Yamada, A., Tawada, K.: Fluctuation of actin sliding over myosin thick filaments in vitro. Biophysics 1, 45–53 (2005)
Yokota, E., Tominaga, M., Mabuchi, I., Tsuji, Y., Staiger, C.J., Oiwa, K., Shimmen, T.: Plant villin, lily P-135-ABP, possesses G-actin binding activity and accelerates the polymerization and depolymerization of actin in a Ca2 + sensitive manner. Plant & Cell Physiology 46, 1690–1703 (2005)
Liu, J.Q., Oiwa, K.: A dynamical network model inspired by molecular motors. In: The 9th International Conference on Systems Biology, Goeterberg, Sweden (August 2008)
Liu, J., Oiwa, K.: A note on a mathematical model for computational moleware communications based on molecular motors. IPSJ SIG Technical Report, 2008(17), 145–148 (2008)
Liu, J.Q., Shimohara, K.: Biomolecular Computation for Bionanotechnology. Artech House, Boston (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 ICST Institute for Computer Science, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, JQ., Nakano, T. (2009). Quantitative Analysis of the Feedback of the Robust Signaling Pathway Network of Myosin V Molecular Motors on GluR1 of AMPA in Neurons: A Networking Approach for Controlling Nanobiomachines. In: Schmid, A., Goel, S., Wang, W., Beiu, V., Carrara, S. (eds) Nano-Net. NanoNet 2009. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 20. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04850-0_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04850-0_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04849-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04850-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)