Abstract
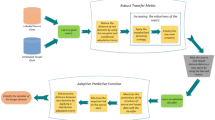
In recent years, transfer learning has attracted much attention in multimedia. In this paper, we propose an efficient transfer dimensionality reduction algorithm called transfer discriminative Logmaps (TDL). TDL finds a common feature so that 1) the quadratic distance between the distribution of the training set and that of the testing set is minimized and 2) specific knowledge of the training samples can be conveniently delivered to or shared with the testing samples. Drawing on this common feature in the representation space, our objective is to develop a linear subspace in which discriminative and geometric information can be exploited. TDL adopts the margin maximization to identify discriminative information between different classes, while Logmaps is used to preserve the local-global geodesic distance as well as the direction information. Experiments carried out on both synthetic and real-word image datasets show the effectiveness of TDL for cross-domain face recognition and web image annotation.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkin, M., et al.: Laplacian Eigenmaps and Spectral Techniques for Embedding and Clustering. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14, 585–591 (2001)
Belhumeur, P., et al.: Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using Class Specific Linear Projection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 19, 711–720 (1997)
Brun, A., et al.: Fast manifold learning based on riemannian normal coordinates. In: Kalviainen, H., Parkkinen, J., Kaarna, A. (eds.) SCIA 2005. LNCS, vol. 3540, pp. 920–929. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cai, D., et al.: Semi-supervised Discriminant Analysis. In: Proc. IEEE ICCV, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Caruana, R., et al.: Multitask Learning. Machine Learning, 41–75 (1997)
Chua, T.S., et al.: NUS-WIDE: A Real-World Web Image Database from National University of Singapore. In: Proc. CIVR (2009)
Dai, W., et al.: Boosting for transfer learning. In: Proc. ICML, pp. 193–200 (2007)
Dai, W., et al.: Self-taught clustering. In: Proc. ICML, pp. 200–207 (2008)
Do, C., et al.: Transfer learning for text classification. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18 (2005)
Fisher, R.A., et al.: The Use of Multiple Measurements in Taxonomic Problems. Annals of Eugenics 7, 179–188 (1936)
He, X., et al.: Locality Preserving Projections. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16 (2004)
Hotelling, H., et al.: Analysis of A Complex of Statistical Variables into Principal Components. Journal of Educational Psychology 24, 417–441 (1933)
Liu, W., et al.: Transductive Component Analysis. In: Proc. ICDM, pp. 433–442 (2008)
Mark, D., et al.: Feature Design for Transfer Learning. In: Proc. NESCAI (2006)
Pan, S.J., et al.: Transfer Learning via Dimensionality Reduction. In: Proc. AAAI, pp. 677–682 (2008)
Roweis, S.T., et al.: Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction by Locally Linear Embedding. Science 290, 2323–2326 (2000)
Sim, T., et al.: The cmu pose, illumination, and expression (pie) database of human faces. Technical report, CMU-RI-TR-01-02, Carnegie Mellon University (2001)
Tao, D., et al.: Geometric Mean for Subspace Selection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 31(2), 260–274 (2009)
Tao, D., et al.: General Tensor Discriminant Analysis and Gabor Features for Gait Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 29(10), 1700–1715 (2007)
Tenenbaum, J.B., et al.: A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290, 2319–2323 (2000)
Zhang, T., et al.: Patch Alignment for Dimensionality Reduction. IEEE Trans. Knowledge and Data Engineering 21(9), 1299–1313 (2009)
Zhang, T., et al.: Discriminative Locality Alignment. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008, Part I. LNCS, vol. 5302, pp. 725–738. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Zhang, T., et al.: A unifying framework for spectral analysis based dimensionality reduction. In: Proc. IJCNN, pp. 1670–1677 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Si, S., Tao, D., Chan, KP. (2009). Transfer Discriminative Logmaps. In: Muneesawang, P., Wu, F., Kumazawa, I., Roeksabutr, A., Liao, M., Tang, X. (eds) Advances in Multimedia Information Processing - PCM 2009. PCM 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5879. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10467-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10467-1_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-10466-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-10467-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)