Abstract
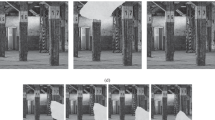
We propose a Bayesian image superresolution method that estimates a high-resolution background image from a sequence of occluded observations. We assume that the occlusions have spatial and temporal continuities. Such assumptions would be plausible, for example, when satellite images are occluded by clouds or when a tourist site is obstructed by people. Although the exact inference of our model is difficult, an efficient superresolution algorithm is derived by using a variational Bayes technique. Experiments show that our superresolution method performs better than existing methods that do not assume the occlusions or that assume the occlusions but do not assume the temporal continuities of the occlusions.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanemura, A., Maeda, S., Ishii, S.: Image superresolution under spatially structured noise. In: IEEE Int. Symp. Signal Processing and Information Technology, December 2007, pp. 275–280 (2007)
Farsiu, S., Robinson, D., Elad, M., Milanfar, P.: Fast and robust multi-frame super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process 13(10), 1327–1344 (2004)
Babacan, D., Molina, R., Katsaggelos, A.: Total variation super resolution using a variational approach. In: IEEE Int. Conf. Image Process, October 2008, pp. 641–644 (2008)
Pickup, L.C., Capel, D.P., Roberts, S.J., Zisserman, A.: Bayesian image super-resolution, continued. In: Advances in NIPS. MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Ivanovski, Z.A., Panovski, L., Karam, L.J.: Robust super-resolution based on pixel-level selectivity. In: Visual Commun. Image Process. Proc. SPIE, vol. 6077, pp. 80–87 (2006)
Melgani, F.: Contextual reconstruction of cloud-contaminated multitemporal multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 44(2), 442–455 (2006)
Golub, G.H., van Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computations, 3rd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fukuda, W., Kanemura, A., Maeda, Si., Ishii, S. (2009). Superresolution from Occluded Scenes. In: Leung, C.S., Lee, M., Chan, J.H. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5864. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10684-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10684-2_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-10682-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-10684-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)