Abstract
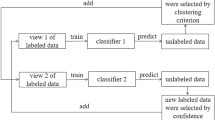
Often in real world applications only a small number of labeled data is available while unlabeled data is abundant. Therefore, it is important to make use of unlabeled data. Co-training is a popular semi-supervised learning technique that uses a small set of labeled data and enough unlabeled data to create more accurate classification models. A key feature for successful co-training is to split the features among more than one view. In this paper we propose new splitting criteria based on the confidence of the views, the diversity of the views, and compare them to random and natural splits. We also examine a previously proposed artificial split that maximizes the independence between the views, and propose a mixed criterion for splitting features based on both the confidence and the independence of the views. Genetic algorithms are used to choose the splits which optimize the independence of the views given the class, the confidence of the views in their predictions, and the diversity of the views. We demonstrate that our proposed splitting criteria improve the performance of co-training.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, X.: Semi-supervised learning literature survey. Technical Report 1530, Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison (2005)
Blum, A., Mitchell, T.: Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of the eleventh annual conference on Computational Learning Theory (COLT 1998), pp. 92–100 (1998)
Nigam, K., Ghani, R.: Analyzing the effectiveness and applicability of co-training. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Information and Knowledge (CIKM 2000), pp. 86–93 (2000)
Feger, F., Koprinska, I.: Co-training using rbf nets and different feature splits. In: Proceedings of 2006 International Joint Conference on Neural Network, pp. 1878–1885 (2006)
Wang, W., Zhou, Z.-H.: Analyzing co-training style algorithms. In: Kok, J.N., Koronacki, J., Lopez de Mantaras, R., Matwin, S., Mladenič, D., Skowron, A. (eds.) ECML 2007. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4701, pp. 454–465. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Opitz, D.: Feature selection for ensembles. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 379–384 (1999)
Goldberg, D.: Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1989)
Kamp, R.G., Savenije, H.H.G.: Optimising training data for anns with genetic algorithms. In: Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., pp. 603–608 (2006)
Asuncion, A., Newman, D.J.: Uci machine learning repository (2007), http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Rebecca Fay, F.S., Kaufmann, U., Palm, G.: Learning object recognition in a neurobotic system. In: Groß, H.-M., Debes, K., Böhme, H.-J. (eds.) 3rd Workshop on SelfOrganization of AdaptiVE Behavior, SOAVE 2004, pp. 198–209 (2004)
Kiritchenko, S., Matwin, S.: Email classification with co-training. In: Proceedings of CASCON 2001, Toronto, Canada, pp. 192–201 (2001)
Terabe, M., Hashimoto, K.: Evaluation criteria of feature splits for co-training. In: Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2008 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Salaheldin, A., El Gayar, N. (2010). New Feature Splitting Criteria for Co-training Using Genetic Algorithm Optimization. In: El Gayar, N., Kittler, J., Roli, F. (eds) Multiple Classifier Systems. MCS 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5997. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12127-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12127-2_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-12126-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-12127-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)