Abstract
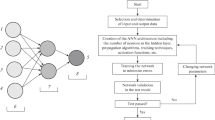
Neural networks are a practical tool for solving various problems of approximation, classification, prediction or control. In the paper we use multilayer perceptrons to determine the character of stress in healthy femur and after endoprosthesoplasty. Inserting metal prosthesis to the bone changes the stress character what can lead to local decalcification and weakening of its strength in certain areas. Dynamic bone load resulting from non-anatomical load can cause fracture in the weak area. Neural network was learned with the data obtained from numerical simulations using the finite element analysis. The input to the network was stress state in twelve points of femur and body mass.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsutz, H.C., Grogoris, P., Dorey, F.J.: Evolution and future of surface replacement of the hip. Journal Orthop. Scj. 3(3) (1998)
Bernakiewicz, M.: Strain Analysis of Femur. In: Biology of Sport 1998, Kokotek k. Lublica, Poland, September 14-16, Vol. 15 (1998) (in Polish)
Bishop, C.M.: Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Oxford University Press Inc., New York (1995)
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern Classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester (2000)
Grigsby, J., Kooken, R., Hershberger, J.: Simulated neural networks to predict outcomes, costs and length of stay among orthopedic rehabilitation patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 75(10), 1077–1081 (1994)
Krzesinski, G., Zagrajek, T.: Modelling Mechanical Properties on Bones. In: Biology of Sport 1997, vol. 17(Suppl. 8), pp. 238–243 (1997) (in Polish)
Mann, K.A., Bartel, D.L., Wright, T.M., Burstein, A.H.: Coulomb frictional interfaces in modeling cemented total hip replacements: a more realistic model. J. Biomech. 28(9), 1067–1078 (1995)
Natali, A.N.: Meroi: A review of the biomechanical properties of bone as material. J. Biomed. Eng. 11, 266–276 (1989)
Nigg, B.M., Herzog, W.: Biomechanics of the muscoskeletal system. J.Wiley&Sons, England (1944)
Nordin, M., Frankel, V.H.: Basic biomechanics of the muscoskeletal system. Lea & Fabiger (1989)
Reilly, D.T., Burstein, A.H.: The mechanical properties of cortical bone. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 56 (1974)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning internal representations by error propagation. In: Rumelhart, D.E., McClelland, J.L., the PDP Research Group (eds.) Parallel Distributed Processing. Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition. Foundations, vol. 1, pp. 318–362. The MIT Press, Cambridge (1986)
Russell, S.J., Norvig, P.: Artificial Intelligence. A Modern Approach. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Korytkowski, M., Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Szarek, A. (2010). Neural Network-Based Assessment of Femur Stress after Hip Joint Alloplasty. In: Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zadeh, L.A., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6113. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13208-7_77
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13208-7_77
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-13207-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-13208-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)