Abstract
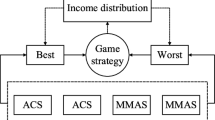
The travelling salesman problem (TSP) is a classic problem of combinatorial optimization and is unlikely to find an efficient algorithm for solving TSPs directly. In the last two decades, ant colony optimization (ACO) has been successfully used to solve TSPs and their associated applicable problems. Despite the success, ACO algorithms have been facing constantly challenges for improving the slow convergence and avoiding stagnation at the local optima. In this paper, we propose a new hybrid algorithm, cooperative ant colony system and genetic algorithm (CoACSGA) to deal with these problems. Unlike the previous studies that regarded GA as a sequential part of the whole searching process and only used the result from GA as the input to the subsequent ACO iteration, this new approach combines both GA and ACS together in a cooperative and concurrent fashion to improve the performance of ACO for solving TSPs. The mutual information exchange between ACS and GA at the end of each iteration ensures the selection of the best solution for the next round, which accelerates the convergence. The cooperative approach also creates a better chance for reaching the global optimal solution because the independent running of GA will maintain a high level of diversity in producing next generation of solutions. Compared with the results of other algorithms, our simulation demonstrates that CoACSGA is superior to other ACO related algorithms in terms of convergence, quality of solution, and consistency of achieving the global optimal solution, particularly for small-size TSPs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flood, M.M.: The traveling salesman problem. Operation Research 4, 61–78 (1955)
Lawer, E.L., Lenstra, J.K., Kan, A.H.R., Shmoys, D.B.: The traveling salesman problem. Wiley, New York (1985)
TSPLIB, http://www.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/groups/comopt/software/TSPLIB95/tsp/
Reinelt, G.: The traveling salesman: computational solutions for TSP applications. Springer, Heidelberg (1994)
Leung, K.S., Jin, H.D., Xu, Z.B.: An expanding self-organizing neural network for the traveling salesman problem. Neurocomputing 6, 267–292 (2004)
Masutti, T.A.S., de Castro, L.N.: A self-organizing neural network using ideas from the immune system to solve the traveling salesman problem. Information Sciences 179, 1454–1468 (2009)
Lo, C.C., Hus, C.C.: Annealing framework with learning memory. IEEE Transactions on System, Man, Cybernetics - Part A 28, 1–13 (1998)
Jayalakshmi, G.A., Sathiamoorthy, S.: A hybrid genetic algorithm – a new approach to solve traveling salesman problem. International Journal of Computational Engineering Science 2, 339–355 (2001)
Yang, J.H., Wu, C.G., Lee, H.P., Liang, Y.C.: Solving traveling salesman problems using generalized chromosome genetic algorithm. Progress in Natural Science 18, 887–892 (2008)
Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., Colorni, A.: The ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics – Part B 26, 29–42 (1996)
Dorigo, M., Gambardella, L.M.: Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 1, 53–66 (1997)
Stutzle, T., Hoos, H.: The MAX-MIN ant system and local search for the traveling salesman problem. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Piscataway, USA, pp. 309–314 (1997)
Stutzle, T., Hoos, H.: MAX-MIN Ant System. Future Generation Computer Systems 16, 889–914 (2000)
Montgomery, J., Randall, M.: The accumulated experience ant colony for the traveling salesman problem. International Journal of Computational Intelligence and Applications 3, 189–198 (2003)
Huang, G.R., Cao, X.B., Wang, X.F.: An ant colony optimization algorithm based on pheromone diffusion. Acta Electronica Sinica 32, 865–868 (2004)
Tsai, C.F., Tsai, C.W., Tseng, C.C.: A new hybrid heuristic approach for solving large traveling salesman problem. Information Sciences 166, 67–81 (2004)
Birattari, M., Pellegrini, P., Dorigo, M.: On the invariance of ant colony optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 11, 732–742 (2007)
Tsutsui, S.: Ant colony optimization with cunning ants. Transactions of Japanese Society for Artificial Intelligence 22, 9–36 (2007)
Cai, Z.Q.: Multi-direction searching ant colony optimization for travelling salesman problem. In: Proceedings of 2008 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, pp. 220–223 (2008)
Ji, J.Z., Huang, Z., Wang, Y.M., Liu, C.N.: A new mechanism of pheromone increment and diffusion for solving travelling salesman problems with ant colony algorithm. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Natural Computation, pp. 558–563 (2008)
Zhang, Y., Li, L.J.: MST ant colony optimization with Lin-Kerninghan local search for the traveling salesman problem. In: proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, pp. 344–347 (2008)
Li, T.K., Chen, W.Z., Zheng, X., Zhang, Z.: An improvement of the ant colony optimization algorithm for solving travelling salesman problem (TSP). In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, pp. 1–3 (2009)
Dorigo, M., Birattari, M., Stutzle, T.: Ant colony optimization: artificial ants as a computational intelligence technique. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine 1, 28–39 (2006)
Pilat, M.L., White, T.: Using genetic algorithms to optimize ACS-TSP. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on ants, Brussels, pp. 282–287 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dong, G., Guo, W.W. (2010). A Cooperative Ant Colony System and Genetic Algorithm for TSPs. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Tan, K.C. (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence. ICSI 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6145. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13495-1_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13495-1_73
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-13494-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-13495-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)