Abstract
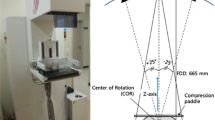
Breast tomosynthesis is a promising technology for breast imaging. Although existing tomosynthesis systems using detector technology developed for FFDM and uniform acquisition parameters have demonstrated the potential to improve the effectiveness of breast screening, the full potential of tomosynthesis is yet to be realised. The effectiveness of tomosynthesis depends on multiple factors, including acquisition geometry, number of projections, reconstruction software and X-ray detector performance. In this study, the authors investigated the use of a specially designed 29 cm x 23 cm CMOS flat panel X-ray detector with a novel Active Pixel Sensor with high spatial resolution, high speed read-out, low noise, negligible image lag and a unique ability to reconfigure imaging parameters such as resolution and gain during an acquisition. Advanced tomosynthesis acquisition methods were used with the new detector including non-uniform spacing of projection views. This combination of optimised X-ray detector and optimised acquisition methods provides enhanced imaging performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niklason, L., et al.: Digital tomosynthesis in breast imaging. Radiology 205, 399–406 (1997)
Dobbins, J.T., Godfrey, D.J.: Digital x-ray tomosynthesis: Current state of the art and clinical potential. Phys. Med. Biol. 48, R65–R106 (2003)
Maidment, A.D.A., Ullberg, C., Francke, T., Lindqvist, L., Sokolov, S., Lindman, K., Adelow, L., Sunden, P.: Clinical evaluation of a photon-counting tomosynthesis mammography system. In: Astley, S.M., Brady, M., Rose, C., Zwiggelaar, R. (eds.) IWDM 2006. LNCS, vol. 4046, pp. 144–151. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Wu, T., et al.: Tomographic mammography using a limited number of low-dose cone-beam projection images. Med. Phys. 30(3), 365–380 (2003)
Zhang, Y., et al.: Investigation of Different PV Distributions in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Mammography. In: Krupinski, E.A. (ed.) IWDM 2008. LNCS, vol. 5116, pp. 593–600. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Marshall, N.W.: A comparison between objective and subjective image quality measurements for a full field digital mammography system. Phys. Med. Biol. 51, 2441–2463 (2006)
Janesick, J.: Photon Transfer. SPIE Press Book (2007)
Kastanis, I., Arridge, S., Stewart, A., Gunn, S., Ullberg, C., Francke, T.: 3D Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Using Total Variation Regularization. In: Krupinski, E.A. (ed.) IWDM 2008. LNCS, vol. 5116, pp. 621–662. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Ren, B., Ruth, C., Stein, J., Smith, A., Shaw, I., Jing, Z.: Design and performance of the prototype full field breast tomosynthesis system with selenium-based flat panel detector. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, vol. 5745, pp. 550–561 (2005)
Bissonnette, M., Hansroul, M., Masson, E., Savard, S., Cadieux, S., Warmoes, P., Gravel, D., Agopyan, J., Polischuk, B., Haerer, W., Mertelmeier, T., Lo, J.Y., Chen, Y., Dobbins III, J.T., Jesneck, J.L., Singh, S.: Digital breast tomosynthesis using an amorphous selenium flat panel detector. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, vol. 5745, pp. 529–540 (2005)
Eberhard, J.W., Albagli, D., Schmitz, A., Claus, B.E.H., Carson, P., Goodsitt, M., Chan, H.-P., Roubidoux, M., Thomas, J.A., Osland, J.: Mammography Tomosynthesis System for High Performance 3D Imaging. In: Astley, S.M., Brady, M., Rose, C., Zwiggelaar, R. (eds.) IWDM 2006. LNCS, vol. 4046, pp. 137–143. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Naday, S. et al. (2010). Optimised Breast Tomosynthesis with a Novel CMOS Flat Panel Detector. In: Martí, J., Oliver, A., Freixenet, J., Martí, R. (eds) Digital Mammography. IWDM 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6136. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13666-5_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13666-5_58
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-13665-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-13666-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)