Abstract
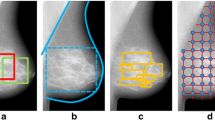
Clinical research has shown that breast cancer risk is strongly related to characteristic mixture of breast tissues as seen on mammographic images. We present an automatic mammographic image segmentation approach, which uses a novel texture signature based methodology, the resultant segmentation can be found useful as a means of aiding radiologists’ estimation in mammographic risk assessment. The developed approach consists of four distinct steps: 1) feature extraction use a stack of small detail annotated mammographic patches, 2) Tabár mammographic building blocks are modelled as texture signatures, 3) model selection and reduction is used to remove noise and possible outliers, and 4) mammographic image segmentation. Visual assessment indicates good and consistent segmentation results. The MIAS database was used in a quantitative and qualitative evaluation with respect to mammographic risk assessment based on both Tabár and Birads risk categories. We found substantial agreement (κ= 0.7 and 0.75 based on Tabár and Birads risk categories, respectively) between classification results and ground truth data. Classification accuracy were 78% and 75% in Tabár and Birads categories, respectively; 86% and 87% in the corresponding low and high categories for Tabár and Birads, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tabár, L., et al.: Breast Cancer: The Art And Science Of Early Detection With Mamography: Perception, Interpretation, Histopatholigic Correlation, 1st edn. Georg Thieme Verlag (2004)
Wolfe, J.N.: Risk for breast cancer development determind by mammographic parenchymal pattern. Cancer 37(5), 2486–2492 (1976)
Guliato, D., et al.: Feature extraction from a signature based on the turning angle function for the classification of breast tumors. Journal of Digital Imaging 21, 129–144 (2008)
Zwiggelaar, R., Taylor, C.J.: Abnormal masses in mammograms: Detection using scale-orientation signatures. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, London, UK, pp. 570–577. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Holmes, A.S., et al.: Transforming pixel signatures into an improved metric space. Image Vision Comput. 20(9-10), 701–707 (2002)
Suckling, J., et al.: The mammographic images analysis society digital mammogram database. In: Dance, Gale, Astley, Gairns (eds.) Excerpta medica. International Congress Series, vol. 1069, pp. 375–378. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1994)
He, W., et al.: Mammographic segmentation based on mammographic parenchymal patterns and spatial moments. In: 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine, p. 115 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, W., Denton, E.R.E., Zwiggelaar, R. (2010). Mammographic Image Segmentation and Risk Classification Using a Novel Texture Signature Based Methodology. In: Martí, J., Oliver, A., Freixenet, J., Martí, R. (eds) Digital Mammography. IWDM 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6136. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13666-5_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13666-5_71
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-13665-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-13666-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)