Abstract
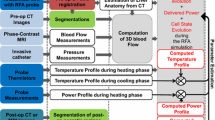
The simulation of radiofrequency ablations (RFA) can predict the achievable coagulation area and thus provide useful information for treatment planning, especially in cases in which the heat distribution can be limited by vascular cooling effects. A strong reliability of the numerical simulation results is essential for clinical use.
In this paper, we present a novel experimental procedure for the verification of RFA simulation systems in a lifelike environment without requiring animal tests. RF ablations are performed within isolated, perfused porcine livers, the corresponding configurations are reconstructed and simulated on a computer, and the resulting pathoanatomical coagulations are compared to their simulated counterparts with consideration of vascular cooling effects. We have applied this procedure for an initial verification of an existing RFA simulation system. The results are presented and discussed in this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization: Fact sheet no. 297 “Cancer” (2009), http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297
Pereira, P.L.: Actual role of radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases. European Radiology 17, 2062–2070 (2007)
Goldberg, S., Gazelle, G., Mueller, P.: Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: A unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR 174, 323–331 (2000)
Lu, D.S.K., Raman, S.S., Vodopich, D.J., Wang, M., Sayre, J., Lassman, C.: Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment of the “heat sink” effect. AJR 178, 47–51 (2002)
Altrogge, I., Preusser, T., Kröger, T., Büskens, C., Pereira, P.-L., Schmidt, D., Peitgen, H.-O.: Multiscale optimization of the probe placement for radiofrequency ablation. Academic Radiology 14, 1310–1324 (2007)
Stein, T.: Untersuchungen zur Dosimetrie der hochfrequenzstrominduzierten interstitiellen Thermotherapie in bipolarer Technik. Fortschritte in der Lasermedizin, vol. 22, Müller and Berlien (2000)
Tungjitkusolum, S., Staelin, S.T., Haemmerich, D., et al.: Three-dimensional finite-element analyses for radio-frequency hepatic tumor ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49, 3–9 (2002)
Villard, C., Soler, L., Gangi, A.: Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: simulation, planning, and contribution of virtual reality and haptics. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering 8, 215–227 (2005)
Kröger, T., Altrogge, I., Preusser, T., Pereira, P.-L., Schmidt, D., Weihusen, A., Peitgen, H.-O.: Numerical Simulation of Radio Frequency Ablation with State Dependent Material Parameters in Three Space Dimensions. In: Larsen, R., Nielsen, M., Sporring, J. (eds.) MICCAI 2006. LNCS, vol. 4191, pp. 380–388. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Berjano, E.J.: Theoretical modeling for radiofrequency ablation: state-of-the-art and challenges for the future. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 5 (2006)
Frericks, B.B., Ritz, J.P., Albrecht, T., Valdeig, S., Schenk, A., Wolf, K.J., Lehmann, K.: Influence of intrahepatic vessels on volume and shape of percutaneous thermal ablation zones: In vivo evaluation in a porcine model. Investigative Radiology 43 (2008)
Lubienski, A., Bitsch, R.G., Lubienski, K., Kauffmann, G., Duex, M.: Radiofrequency ablation (rfa): Development of a flow model for bovine livers for extensive bench testing. CardioVascular and Interventional Radiology 29, 1068–1072 (2006)
Arrhenius, S.: Über die Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit bei der Inversion von Rohrzucker durch Säuren. Z. Phys. Chem. 4, 226–248 (1887)
Weihusen, A., Ritter, F., Kröger, T., Preusser, T., Zidowitz, S., Peitgen, H.-O.: Workflow oriented software support for image guided radiofrequency ablation of focal liver malignancies. In: Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6509, p. 650919 (2007)
Zidowitz, S., Drexl, J., Kröger, T., Preusser, T., Ritter, F., Weihusen, A., Peitgen, H.-O.: Bayesian Vessel Extraction for Planning of Radiofrequency-Ablation. In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin, pp. 187–191. Springer, Berlin (2007)
OPTIMIST Handelsges.m.b.H., Austria, http://www.optimist.at
RF-applicator CelonPro Surge 200-T40, Celon AG medical instruments, Germany, http://www.celon.de
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Weihusen, A. et al. (2010). Towards a Verified Simulation Model for Radiofrequency Ablations. In: Navab, N., Jannin, P. (eds) Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions. IPCAI 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6135. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13711-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13711-2_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-13710-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-13711-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)