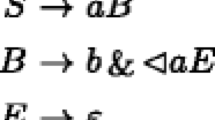Abstract
Usually, a parser for an LR(k)-grammar G is a deterministic pushdown transducer which produces backwards the unique rightmost derivation for a given input string x ∈ L(G). The best known upper bound for the size of such a parser is \(O(2^{|G||\Sigma|^{k+1}})\) where |G| and |Σ| are the sizes of the grammar G and the terminal alphabet Σ, respectively. If we add to a parser the possibility to manipulate a directed graph of size O(|G|n) where n is the length of the input then we obtain an extended parser. The graph is used for an efficient parallel simulation of all potential leftmost derivations of the current right sentential form such that the unique rightmost derivation of the input can be computed. Given an arbitrary LR(k)-grammar G, we show how to construct an extended parser of O(|G| + #LA |N|2k k logk) size where |N| is the number of nonterminal symbols and #LA is the number of possible lookaheads with respect to the grammar G. As the usual parser, this extended parser uses only tables as data structure. Using some ingenious data structures and increasing the parsing time by a small constant factor, the size of the extended parser can be reduced to O(|G| + #LA|N|k 2). The parsing time is O(ld(input) + k|G|n) where ld(input) is the length of the derivation of the input. Moreover, we have constructed a one pass parser.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho, A.V., Ullman, J.D.: The Theory of Parsing, Translation, and Compiling. Parsing, vol. I. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1972)
Blum, N.: Theoretische Informatik: Eine anwendungsorientierte Einführung. Oldenbourg Verlag (1998)
Blum, N.: On parsing LL-languages. TCS 267, 49–59 (2001)
Blum, N.: On LR(k)-parsers of polynomial size, Research report No. 85308, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Bonn (2010), http://theory.cs.uni-bonn.de/blum/papers/lr4.pdf
Chapman, N.P.: LR Parsing: Theory and Practice. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1987)
DeRemer, F.L.: Practical Translators for LR(k) Languages. Ph.D. Thesis, MIT, Harvard, Mass (1969)
Earley, J.: An efficient context-free parsing algorithm. CACM 13, 94–102 (1970)
Grune, D., Jacobs, C.J.H.: Parsing Techniques: A Practical Guide, 2nd edn. Monographs in Computer Science. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Sippu, S., Soisalon-Soininen, E.: Parsing Theory, vol. I: Languages and Parsing. EATCS Monographs on Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 15. Springer, Heidelberg (1988)
Sippu, S., Soisalon-Soininen, E.: Parsing Theory, vol. II: LR(k) and LL(k) Parsing. EATCS Monographs on Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 20. Springer, Heidelberg (1990)
Tomita, M.: An efficient context-free parsing algorithm for natural languages. In: IJCAI, pp. 756–764 (1985)
Ukkonen, E.: Lower bounds on the size of deterministic parsers. JCSS 26, 153–170 (1983)
Wilhelm, R., Maurer, D.: Compiler Design. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Blum, N. (2010). On LR(k)-Parsers of Polynomial Size. In: Abramsky, S., Gavoille, C., Kirchner, C., Meyer auf der Heide, F., Spirakis, P.G. (eds) Automata, Languages and Programming. ICALP 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6199. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14162-1_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14162-1_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-14161-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-14162-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)