Abstract
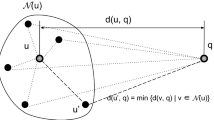
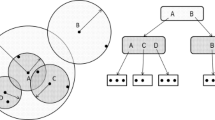
Finding the closest object for a query in a database is a classical problem in computer science. For some modern biological applications, computing the similarity between two objects might be very time consuming. For example, it takes a long time to compute the edit distance between two whole chromosomes and the alignment cost of two 3D protein structures. In this paper, we study the nearest neighbor search problem in metric space, where the pair-wise distance between two objects in the database is known and we want to minimize the number of distances computed on-line between the query and objects in the database in order to find the closest object. We have designed two randomized approaches for indexing metric space databases, where objects are purely described by their distances with each other. Analysis and experiments show that our approaches only need to compute O(logn) objects in order to find the closest object, where n is the total number of objects in the database.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., Lipman, D.J.: Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402 (1997)
Pearson, W.R., Lipman, D.J.: Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 85(8), 2444–2448 (1988)
Guo, F., Wang, L., Yang, Y.: Efficient Algorithms for 3D Protein Substructure Identification. In: The 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE 2010 (accepted 2010)
Ciaccia, P., Patella, M., Zezula, P.: M-tree: An Efficient Access Method for Similarity Search in Metric Spaces. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB 1997), pp. 426–435 (August 1997)
Navarro, G.: Searching in Metric Spaces by Spatial Approximation. The VLDB Journal 11, 28–46 (2002)
Marvin, S.: The choice of reference points in best-match file searching. Communnications of the ACM 20, 339–343 (1977)
Micó, M.L., Oncina, J., Vidal, E.: A new version of the nearest-neighbour approximating and eliminating search algorithm (AESA) with linear preprocessing time and memory requirements. Pattern Recognition Letters 15, 9–17 (1994)
Filho, R.F.S., Traina, A.J.M., Traina Jr., C., Faloutsos, C.: Similarity search without tears: the OMNI-family of all-purpose access methods. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE 2001), pp. 623–630 (2001)
Bustos, B., Navarro, G., Chávez, E.: Pivot selection techniques for proximity searching in metric spaces. Pattern Recognition Letters 24, 2357–2366 (2003)
Rico-Juan, J.R., Micó, L.: Comparison of AESA and LAESA search algorithms using string and tree-edit-distances. Pattern Recognition Letters 24, 1417–1426 (2003)
Digout, C., Nascimento, M.A., Coman, A.: Similarity search and dimensionality reduction: Not all dimensions are equally useful. In: Lee, Y., Li, J., Whang, K.-Y., Lee, D. (eds.) DASFAA 2004. LNCS, vol. 2973, pp. 831–842. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Vidal, E.: An algorithm for finding nearest neighbours in (approximately) constant average time. Pattern Recognition Letters 4, 145–157 (1986)
Zezula, P., Amato, G., Dohnal, V., Batko, M.: Similarity Search: The Metric Space Approach. Advances in Database Systems, vol. 32. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Li, M., Ma, B., Wang, L.: On the closest string and substring problems. Journal of the ACM 49, 157–171 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, L., Yang, Y., Lin, G. (2010). Randomized Approaches for Nearest Neighbor Search in Metric Space When Computing the Pairwise Distance Is Extremely Expensive. In: Chen, B. (eds) Algorithmic Aspects in Information and Management. AAIM 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6124. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14355-7_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14355-7_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-14354-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-14355-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)