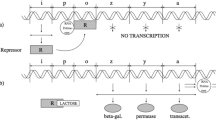
Abstract
Modelling activities in molecular biology face the difficulty of prediction to link molecular knowledge with cell phenotypes. Even when the interaction graph between molecules is known, the deduction of the cellular dynamics from this graph remains a strong corner stone of the modelling activity, in particular one has to face the parameter identification problem. This article is devoted to convince the reader that computers can be used not only to simulate a model of the studied biological system but also to deduce the sets of parameter values that lead to a behaviour compatible with the biological knowledge (or hypotheses) about dynamics. This approach is based on formal logic. It is illustrated in the discrete modelling framework of genetic regulatory networks due to René Thomas.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, J., Bourdon, J., Eveillard, J., Fromentin, D., Roux, O., Sinoquet, C.: Temporal constraints of a gene regulatory network: refining a qualitative simulation. Biosystems 98(3), 149–159 (2009)
Bernot, G., Comet, J.-P., Khalis, Z.: Gene regulatory networks with multiplexes. In: European Simulation and Modelling Conference Proceedings, France, October 27-29, pp. 423–432 (2008) ISBN 978-90-77381-44-1
Bernot, G., Gaudel, M.C., Marre, B.: Software testing based on formal specifications: A theory and a tool. Software Engineering Journal 6(6), 387–405 (1991)
Cardelli, L., Caron, E., Gardner, P., Kahramanogulları, O., Phillips, A.: A process model of rho gtp-binding proteins. Theoretical Computer Science 410(33-34), 3166–3185 (2009)
Cimatti, A., Clarke, E., Giunchiglia, E., Giunchiglia, F., Pistore, M., Roveri, M., Sebastiani, R., Tacchella, A.: NuSMV Version 2: An OpenSource Tool for Symbolic Model Checking. In: Brinksma, E., Larsen, K.G. (eds.) CAV 2002. LNCS, vol. 2404, p. 359. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Collado-Vides, J., Magasanik, B., Smith, T.: Integrative approaches to molecular biology. The MIT press, Cambridge (1996)
Curti, M., Degano, P., Priami, C., Baldari, C.T.: Modelling biochemical pathways through enhanced π-calculus. Theoretical Computer Science 325(1), 111–140 (2004)
de Jong, H.: Qualitative modeling and simulation of bacterial regulatory networks. In: Heiner, M., Uhrmacher, A. (eds.) CMSB 2008. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 5307, p. 1. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Fanchon, E., Corblin, F., Trilling, L., Hermant, B., Gulino, D.: Modeling the molecular network controlling adhesion between human endothelial cells: Inference and simulation using constraint logic programming. In: Danos, V., Schachter, V. (eds.) CMSB 2004. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3082, pp. 104–118. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Gouzé, J.-L.: Positive and negative circuits in dynamical systems. Journal of Biological Systems 6, 11–15 (1998)
Jacob, F., Monod, J.: Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. Journal of molecular biology 3, 318–356 (1961)
Jard, C., Jéron, T.: TGV: theory, principles and algorithms. a tool for the automatic synthesis of conformance test cases for non-deterministic reactive systems. Software Tools for Technology Transfert 7(4), 297–315 (2005)
Khalis, Z., Bernot, G., Comet, J.-P.: Gene Regulatory Networks: Introduction of multiplexes into R. Thomas’ modelling. In: Proc. of the Nice Spring school on Modelling and simulation of biological processes in the context of genomics, EDP Science, pp. 139–151 (2009) ISBN : 978-2-7598-0437-5
Khalis, Z., Comet, J.-P., Richard, A., Bernot, G.: The smbionet method for discovering models of gene regulatory networks. Genes, Genomes and Genomics (2009)
Kügler, P., Gaubitzer, E., Müller, S.: Parameter identification for chemical reaction systems using sparsity enforcing regularization: A case study for the chlorite-iodide reaction. Journal of Physical Chemistry A 113(12), 2775–2785 (2009)
Little, J.W.: Threshold effects in gene regulation: When some is not enough. PNAS 102(15), 5310–5311 (2005)
Mateus, D., Gallois, J.-P., Comet, J.-P., Le Gall, P.: Symbolic modeling of genetic regulatory networks. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology 5(2B), 627–640 (2007)
Naldi, A., Remy, E., Thieffry, D., Chaouiya, C.: A reduction of logical regulatory graphs preserving essential dynamical properties. In: Degano, P., Gorrieri, R. (eds.) CMSB 2009. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 5688, pp. 266–280. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Plahte, E., Mestl, T., Omholt, S.W.: Feedback loops, stability and multistationarity in dynamical systems. Journal Biological Systems 3, 409–413 (1995)
Popper, K.R.: Conjectures and refutations: the growth of scientific knowledge. Routledge & Kegan Paul, London (1965)
Richard, A., Comet, J.-P.: Necessary conditions for multistationarity in discrete dynamical systems. Discrete Applied Mathematics 155(18), 2403–2413 (2007)
Rizk, A., Batt, G., Fages, F., Soliman, S.: A general computational method for robustness analysis with applications to synthetic gene networks. Bioinformatics 25(12), i169–i178 (2009)
Siebert, H., Bockmayr, A.: Temporal constraints in the logical analysis of regulatory networks. Theoretical Computer Science 391(3), 258–275 (2008)
Snoussi, E.H.: Necessary conditions for multistationarity and stable periodicity. Journal of Biological Systems 6, 3–9 (1998)
Snoussi, E.H.: Qualitative dynamics of a piecewise-linear differential equations: a discrete mapping approach. Dynamics and stability of Systems 4, 189–207 (1989)
Snoussi, E.H., Thomas, R.: Logical identification of all steady states: the concept of feedback loop caracteristic states. Bull. Math. Biol. 55(5), 973–991 (1993)
Soulé, C.: Graphical requirements for multistationarity. ComPlexUs 1, 123–133 (2003)
Thomas, R.: On the relation between the logical structure of systems and their ability to generate multiple steady states and sustained oscillations. In: Series in Synergetics, vol. 9, pp. 180–193. Springer, Heidelberg (1981)
Thomas, R., d’Ari, R.: Biological Feedback. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bernot, G., Comet, JP. (2010). On the Use of Temporal Formal Logic to Model Gene Regulatory Networks. In: Masulli, F., Peterson, L.E., Tagliaferri, R. (eds) Computational Intelligence Methods for Bioinformatics and Biostatistics. CIBB 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6160. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14571-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14571-1_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-14570-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-14571-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)