Abstract
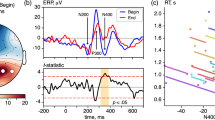
The purpose of this study was to apply recurrence plots and recurrence quantification analysis (RQA) on event related potentials (ERPs) recorded during memory recognition tests. Data recorded during memory retrieval in four scalp region was used. Tow most important ERP’s components corresponding to memory retrieval, FN400 and LPC, were detected in recurrence plots computed for single-trial EEGs. In addition, the RQA was used to quantify changes in signal dynamic structure during memory retrieval, and measures of complexity as RQA variables were computed. Given the stimulus, amplitude of the RQA variables increases around 400ms, corresponding to dimension reduction of system. Furthermore, after 800ms these amplitudes decreased which can be as a consequence of an increase in system dimension and back to its basic state. The mean amplitude of Old items was more than New one.
Using this method, we found its ability to detect memory components of EEG signals and do a distinction between Old/ New items. In contrast with linear techniques recurrence plots and RQA do not need large number of recorded trials, and they can indicate changes in even single-trial EEGs. RQA can also show differences between old and new events in a memory process.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donchin, E., Ritter, W., McCallum, C.: Cognitive psychophysiology: the endogenous components of the ERP. In: Callaway, E., Tueting, P., Koslow, S. (eds.) Event-related potentials in man, pp. 349–441. Academic Press, New York (1978)
Friedman, D., Johnson Jr., R.: Event-related potential (ERP) studies of memory encoding and retrieval: a selective review. Microsc. Res. Tech. 51, 6–28 (2000)
Rugg, M.D., Allan, K.: Memory retrieval: an electrophysiological perspective. In: The new cognitive neurosciences, 2nd edn., pp. 805–816. MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Jacoby, L.L.: A process dissociation framework: separating automatic from intentional uses of memory. J. Mem. Lang. 30, 513–541 (1991)
Reder, L.M., Nhouyvanisvong, A., Schunn, C.D., Ayers, M.S., Angstadt, P., Hiraki, K.: A mechanistic account of the mirror effect for word frequency: a computational model of remember-know judgments in a continuous recognition paradigm. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 26, 294–320 (2000)
Yonelinas, A.P., Mem Lang, J.: J. Mem. Lang. The nature of recollection and familiarity: a review of 30 years of research 46, 441–517 (2002)
Curran, T., DeBuse, C., Woroch, B., Hirshman, E.: Combined Pharmacological and Electrophysiological Dissociation of Familiarity and Recollection. Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive: The Journal of Neuroscience 26(7) (2006)
Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessel, T.M.: Essentials of Neural Science and Behavior (1995) (Appleton & Lange, East Norwalk, Connecticut)
Kutas, M., van Petten, C.: Psycholinguistics electrified: event related potential investigations. In: Gensbacher, M.A. (ed.) Handbook of psycholinguistics, pp. 83–143. Academic Press, San Diego (1994)
Amit, D.J.: Modeling Brain Function. The World of Attractor Neural Networks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
P.L.: Electric Fields of the Brain. Oxford University Press, NY (1981)
Longtin, A., Galdrikian, B., Farmer, B., Theiler, J., Eubank, S.: Testing for nonlinearity in time series: The method of surrogate data. Physica D 58, 77–94 (1992)
Babloyantz, A., Salazar, J.M., Nicolis, C.: Evidence of chaotic dynamics of brain activity during the sleep cycle. Phys. Lett. A 111, 152–156 (1985)
Gallez, D., Babloyantz, A.: Predictability of human EEG: A dynamical approach. Biol. Cybern. 64, 381–391 (1991)
Rapp, P.E., Zimmerman, I.D., Albano, A.M., de Guzman, G.C., Greenbaun, N.N., Bashore, T.R.: Experimental studies of chaotic neural behavior: Cellular activity and electroencephalographic signals. In: Othmer, H.G. (ed.) Nonlinear Oscillations in Biology and Chemistry. Lecture Notes in Biomathematics, vol. 66, pp. 175–205. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Lutzenberger, W., Elbert, T., Birbaumer, N., Ray, W.J., Schupp, H.: The scalp distribution of the fractal dimension of the EEG and its variation with mental tasks. Brain Topogr. 5, 27–33 (1992)
Pritchard, W.S., Duke, D.W.: Dimensional analysis of no-task human EEG using the Grassberger-Procaccia method. Psychophysiol. 29, 182–191 (1992)
Sutton, S., Braren, M., Zubin, J., John, E.R.: Evoked potential correlates of stimulus uncertainty. Science 150, 1187–1188 (1965)
Wong, K.F.K., Galka, A., Yamashitad, O., Ozaki, T.: Modelling non-stationary variance in EEG time series by state space GARCH model. Computers in Biology and Medicine (2005)
Wong, K.K.F.: Modelling non-stationary variance in EEG time series by state space GARCH model
Thomasson, N., Hoeppner, T.J., Webber Jr., C.L., Zbilut, J.P.: Recurrence quantification in epileptic EEGs. Phys. Lett. A 279(1-2), 94–101 (2001)
Marwan, N., Meinke, A.: J. Bifur.Extended recurrence plot analysis and its application to ERP data. Chaos Cogn. Int. Complex Brain Dynam. 14, 761–771 (2004)
Schinkel, S., Marwan, N., Kurths, J.: Order patterns recurrence plots in the analysis of ERP data. Cogn. Neurodyn. 1, 317–325 (2007)
Eckmann, J.-P., Kamphorst, S.O., Ruelle, D.: Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys 5, 973–977 (1987)
Takens, F.: Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In: Rand, D., Young, L.-S. (eds.) Dynamical Systems and Turbulence. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 898, pp. 366–381. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Packard, N.H., Crutchfield, J.P., Farmer, J.D., Shaw, R.S.: Geometry from a time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 712–716 (1980)
Webber Jr., C.L., Zbilut, J.P.: Dynamical assessment of physiological systems and states using recurrence plot strategies. J. Appl. Physiol. 76, 956–973 (1994)
Marwan, N., Wessel, N., Meyerfeldt, U., Schirdewan, A., Kurths, J.: Recurrence plot based measures of complexity and its application to heart rate variability data. Phys. Rev. E, 66(2) (2002)
Theiler, J.: Spurious dimension from correlation algorithms applied to limited time-series data. Phys. Rev. A 34, 2427–2432 (1986)
Kozma, R., Freeman, W.J., Erdi, P.: The KIV model—nonlinear sp spatio-temporal dynamics of the primordial vertebrate forebrain. Neurocomputing 52-54, 819–826 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Talebi, N., Nasrabadi, A.M. (2010). Recurrence Plots for Identifying Memory Components in Single-Trial EEGs. In: Yao, Y., Sun, R., Poggio, T., Liu, J., Zhong, N., Huang, J. (eds) Brain Informatics. BI 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6334. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15314-3_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15314-3_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15313-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15314-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)