Abstract
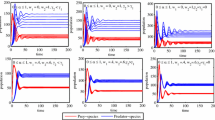
The control of plagues is the regulation and the handling of some species referred to as plagues, normally these are species that affect the ecology and the economy of a certain location. The search for solutions to the important economic incidence of the plagues in the croppings has had an evolution throughout the last two decades. In the studies of population dynamics of plagues in croppings, it is fundamental to consider the predator-prey systems. We formulated a fuzzy cellular model for modeling predator-prey interactions and to study the control of plagues in a croppings of pepper affected by Frankliniella species. We consider as predators for the biological control of these plagues two species to the Orius species. Our model can be used to calculate the introduction of natural enemies (predators) for fighting against the injurious species (preys). The results show that the proposed model works as a tool to achieve plagues control. The combination of predator and prey numbers allows us to stabilize the pepper density level on a suitable bio-economic equilibrium level.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batal, K., Smittle, D.: Response of bell pepper to irrigation, nitrogen, and plant-population. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 106, 259–262 (1981)
Cebula, S.: Otimization of plant and shoot spacing in greenhouse production of sweet pepper. Acta Hort. 412, 321–329 (1995)
Cruz-Huerta, N., Sanchez del Castillo, F., Ortiz-Cereceres, J., Mendoza-Castillo, M.: High plant stand with early pruning on yield and harvest period in bell pepper. Agricultura Tecnica en Mexico 31(1), 73–80 (2009)
Decoteau, D., Graham, H.: Plant spatial arrangement affects growth, yield, and pod distribution of cayenne peppers. Hortsci 29, 149–151 (1994)
Edelstein-Keshet, L.: Mathematical Models in Biology. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York (1987)
Gamez, M., Carreno, R., Andujar, A., Barranco, P., Cabello, T.: Modelos matematicos de depredator-presa en cultivos horticolas en invernadero en el sudeste de la peninsula iberica. Biol. San. Veg. Plagas 26, 665–672 (2002)
Gotelli, N.: A primer of Ecology. Sinauer Associates (1998) (incorporated)
Huang, Z., Chen, S., Xia, Y.: Incorporate intelligence into an ecological system: An adaptive fuzzy control approach. Applied Mathematics and Computation 177, 243–250 (2006)
Schaefer, J.A., Wilson, C.: The fuzzy structure of populations. Can. J. Zool. 80, 2235–2241 (2002)
Leal-Ramírez, C., Castillo, O., Rodríguez-Díaz, A.: Fuzzy cellular model applied to the dynamics of a uni-specific population induced by environment variations. In: Proceedings of Ninth Mexican International Conference on Computer Science, pp. 210–220 (2008)
Lorenzo, P., Castilla, N.: Bell pepper yield response to plant density and radiation in unheated plastic greenhouse. Acta Hort. 412, 330–334 (1995)
Lotka, A.: Elements of physical biology. Williams and Wilkins Co (1925)
Malthus, T.R.: An Essay on the Principle of Population. London (1798)
Mendel, J.: Uncertain Rule-Based Fuzzy Logic Systems: Introduction and New Directions. Prentice-Hall, NJ (2001)
Mills, N., Getz, W.: Modelling the biological control of insect pests: a review of host-parasitoid models. Ecological Modelling 92, 121–143 (1996)
Morales, J., Buranr, J.V.: Interactions between cycloneda sanhuine and the brown citrus aphid: adult feeding and larval mortality. Environ. Entomol. 14(4), 520–522 (1985)
Murray, J.: Mathematical Biology. Springer, Berlin (1990)
Sadhukhan, D., Sahoo, L., Mondal, B., Maiti, M.: Food chain model with optimal harvesting in fuzzy environment. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 1(2), 1–2 (2009)
Stoffella, P., Bryan, H.: Plant population influences growth and yields of bell pepper. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 113, 835–839 (1998)
Tuchin, P.: Does population ecology have general laws? Oikos 94, 17–26 (2001)
Verlhust, P.: Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accrossement. Corr. Math. Phys. 10, 113–121 (1932)
Volterra, V.: Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. Mem. R. Accad. Naz. dei Lincei. Ser. VI 2 (1926)
Zadeh, L.: Fuzzy sets. Inform. Control 8, 338–353 (1965)
Zadeh, L.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning, parts 1, 2, and 3. Information Sciences 8, 199–249, 301–357 (1975)
Zadeh, L.: Fuzzy logic. Computer 1(4), 83–93 (1988)
Zavala, M., Diaz-Sierra, R., Purves, D., Zea, G., Urbieta, I.: Modelos espacialmente explicitos. Ecosistemas 15(3), 88–99 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Leal-Ramirez, C., Castillo, O., Rodriguez-Diaz, A. (2010). Fuzzy Cellular Model for Predator-Prey Interaction Applied to the Control of Plagues in a Peppers Cropping. In: Castillo, O., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W. (eds) Soft Computing for Intelligent Control and Mobile Robotics. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 318. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15534-5_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15534-5_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15533-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15534-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)