Abstract
Laser ablation is the process of removing material with very intensive, pulsed laser radiation. It is a technology which gains increasingly greater importance for drilling, eroding, welding, structuring and marking of all kinds of materials.
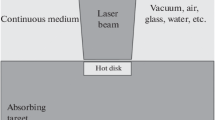
We study the process of laser ablation in a combined approach of molecular dynamics simulations and direct continuum modelling of the electron heat conduction. The method, boundary conditions and benchmarks are presented.
We present ablation studies of aluminium and determine the ablation threshold, the melting dependence on pulse properties and cluster analysis of the evaporated material. We also study laser ablation of a complex anisotropic alloy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimov, S.I., Kapeliovich, B.L., Perel’man, T.L., Electron emission from metal surfaces exposed to ultra short laser pulses. J. Exp. Theo. Phys. Lett. 39 (1974)
Stadler, J., Mikulla, R., Trebin, H.-R., IMD: A software package for molecular dynamics studies on parallel computers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 8, 1131–1140 (1997)
Roth, J., Gähler, F., Trebin, H.-R., A molecular dynamics run with 5.180.116.000 particles. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 11, 317–322 (2000)
Mishin, Y., Farkas, D., Mehl, M.J., Papaconstantopoulos, D.A., Interatomic potentials for monoatomic metals from experimental data and ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. B 59, 3393–3407 (1999)
Ercolessi, F., Adams, J.B., Interatomic potentials from first-principles calculations: The force-matching method. Europhys. Lett. 26, 583–588 (1994)
Brommer, P., Gähler, F., Potfit: effective potentials from ab-initio data. Mod. Sim. Mat. Sci. Eng. 15, 295–304 (2007)
Brommer, P., Development and Test of Interaction potentials for complex metallic alloys. PhD Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart (2009)
Sonntag, S., Roth, J., Gähler, F., Trebin, H.-R., Femtosecond laser ablation of aluminum. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9742–9744 (2009)
Sonntag, S., Roth, J., Trebin, H.-R., Molecular dynamics simulations of laser ablation in orthorhombic Al13Co4. Appl. Phys. A (2010). http://www.springerlink.com/index/10.1007/s00339-010-5762-5
Sonntag, S., Roth, J., Trebin, H.-R., Molecular dynamics simulations of laser ablation in Aluminum. In preparation
Grottel, S., Reina, G., Vrabec, J., Ertl, T., Visual verification and analysis of cluster detection for molecular dynamics. IEEE Trans. on Visual. and Comp. Graph. 13, 1624–1631 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Roth, J., Trichet, C., Trebin, HR., Sonntag, S. (2011). Laser Ablation of Metals. In: Nagel, W., Kröner, D., Resch, M. (eds) High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering '10. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15748-6_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15748-6_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15747-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15748-6
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)