Abstract
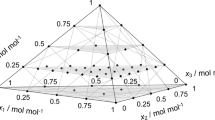
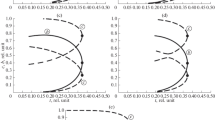
Predictions of the transport properties self-diffusion coefficient and shear viscosity are presented for a recently developed molecular ammonia model. These data show mean unsigned deviations to the experiment over a temperature range from 200 to 500 K of 8 % for the self-diffusion coefficient and 12% for the shear viscosity. Furthermore, the vapor-liquid equilibria of the ternary system carbon dioxide + cyclohexanol + cyclohexane and its binary subsystems are investigated. The modified Lorentz-Berthelot combination rule with one state-independent binary interaction parameter was used for the pairwise unlike dispersive interactions. Per binary subsystem, the parameter was adjusted to a single experimental vapor pressure. The binary subsystems are in good agreement with experimental data throughout the entire composition range. For the ternary system, the vapor pressure is underpredicted by about 12 %.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M.P. Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulation, Computational Soft Matter, Vol. 23, John von Neumann-Institute for Computing, Julich, 2004
Guevara-Carrion, G., Vrabec, J., Hasse, H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16664.
Impey, R.W., Klein, M.L. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 104, 579.
Sagarik, K.P., Ahlrichs, R., Brode, S. Mol. Phys. 1986, 57, 1247.
Mansour, K.A., Murad, S. Fluid Phase Equil. 1987, 37, 305.
Eckl, B., Vrabec, J., Hasse, H. Mol. Phys. 2008, 106, 1039.
Schnabel, T., Vrabec, J., Hasse, H. in Nagel, W. E.; Jäger, W.; Resch, M. (Eds.). High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering ’05 2006, 319.
Gross, T., Buchhauser, J., Price, W., Tarasov, I.N., Lüdemann, H. J. Mol. Liq. 1997, 73, 433.
Lemmon, E.W., Huber, M.L., McLinden, M.O. Standard Reference Database 23: Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties -REFPROP; NIST: 2007.
Merker T., Guevara-Carrion G., Vrabec J., Hasse H. in Nagel, W. E.; Kröner, D. B.; Resch, M. (Eds.). High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering ‘08 2009, 529.
Vrabec, J., Stoll, J., Hasse, H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001 105, 12126.
Eckl, B., Vrabec, J., Hasse H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008 112, 12710.
Schnabel, T., Vrabec, J., Hasse H. J. Mol. Liq. 2007, 135, 170.
Nagarajan, N., Robinson, R.L. Jr. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1987, 32, 369.
Shibata, S.K., Sandler, S.I. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1989, 34, 419.
Krichevski, I.R., Sorina, G.A. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 34, 679.
Smith, J.M., Van Ness, H.C., Abbott, M.M. Introduction to chemical engineering thermodynamics, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1996.
Chen, J.-T., Lee, M.-J. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1996, 41, 339.
Chevalley, J. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1961, 52, 510.
Mukhapadhay, M., Srinivas, P. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 4713.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vrabec, J., Guevara-Carrion, G., Merker, T., Hasse, H. (2011). Molecular Modeling of Hydrogen Bonding Fluids: Transport Properties and Vapor-Liquid Coexistence. In: Nagel, W., Kröner, D., Resch, M. (eds) High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering '10. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15748-6_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15748-6_39
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15747-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15748-6
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)