Abstract
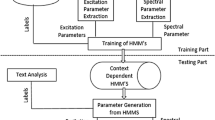
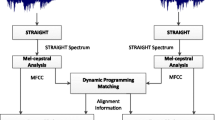
Statistical parametric synthesis offers numerous techniques to create new voices. Speaker adaptation is one of the most exciting ones. However, it still requires high quality audio data with low signal to noise ration and precise labeling. This paper presents an automatic speech recognition based unsupervised adaptation method for Hidden Markov Model (HMM) speech synthesis and its quality evaluation. The adaptation technique automatically controls the number of phone mismatches. The evaluation involves eight different HMM voices, including supervised and unsupervised speaker adaptation. The effects of segmentation and linguistic labeling errors in adaptation data are also investigated. The results show that unsupervised adaptation can contribute to speeding up the creation of new HMM voices with comparable quality to supervised adaptation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, A., Zen, H., Tokuda, K.: Statistical Parametric Speech Synthesis. In: ICASSP 2007, pp. 1229–1232 (2007)
Iwahashi, N., Sagisaka, Y.: Speech Spectrum Conversion Based on Speaker Interpolation and Multi-Functional Representation with Weighting by Radial Basis Function Networks. Speech Communications 16(2), 139–151 (1995)
Tachibana, M., Yamagishi, J., Masuko, T., Kobayashi, T.: Speech Synthesis with Various Emotional Expressions and Speaking Styles by Style Interpolation and Morphing. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E88-D(11), 2484–2491 (2005)
Tamura, M., Masuko, T., Tokuda, K., Kobayashi, T.: Adaptation of Pitch and Spectrum for HMM-Based Speech Synthesis Using MLLR. In: ICASSP 2001, pp. 805–808 (1998)
Ogata, K., Tachibana, M., Yamagishi, J., Kobayashi, T.: Acoustic Model Training Based on Linear Transformation and MAP Modification for HSMM-Based Speech Synthesis. In: ICSLP 2006, pp. 1328–1331 (2006)
Kawai, H., Toda, T., Ni, J., Tsuzaki, M., Tokuda, K.: XIMERA: A New TTS from ATR Based on Corpus-Based Technologies. In: ISCA SSW5 2004, pp. 179–184 (2004)
Plumpe, M., Acero, A., Hon, H.-W., Huang, X.-D.: HMM-Based Smoothing for Concatenative Speech Synthesis. In: ICSLP 1998, pp. 2751–2754 (1998)
Okubo, T., Mochizuki, R., Kobayashi, T.: Hybrid Voice Conversion of Unit Selection and Generation using Prosody Dependent HMM. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E89-D(11), 2775–2782 (2006)
Mihajlik, P., Fegyó, T., Tüske Z., Ircing, P.: A Morpho-graphemic Approach for the Recognition of Spontaneous Speech in Agglutinative Languages like Hungarian. In: Interspeech 2007, pp. 1497–1500 (2007)
King, S., Tokuda, K., Zen, H., Yamagishi, J.: Unsupervised Adaptation for HMM-Based Speech Synthesis. In: Interspeech 2008, pp. 1869–1872 (2008)
Gibson, M.: Two-Pass Decision Tree Construction for Unsupervised Adaptation of HMM-Based Synthesis Models. In: Interspeech 2009, pp. 1791–1794 (2009)
Yamagishi, J., Ling, Z., King, S.: Robustness of HMM-Based Speech Synthesis. In: Interspeech 2008, pp. 581–584 (2008)
Tóth, B., Németh, G.: Hidden Markov Model Based Speech Synthesis System in Hungarian. Infocommunications Journal LXIII(2008/7), 30–34 (2008)
Mihajlik, P., Tarján, B., Tüske, Z., Fegyó, T.: Investigation of Morph-based Speech Recognition Improvements across Speech Genres In: Interspeech 2009, pp. 2687–2690 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tóth, B., Fegyó, T., Németh, G. (2010). Some Aspects of ASR Transcription Based Unsupervised Speaker Adaptation for HMM Speech Synthesis. In: Sojka, P., Horák, A., Kopeček, I., Pala, K. (eds) Text, Speech and Dialogue. TSD 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6231. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15760-8_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15760-8_52
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15759-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15760-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)