Abstract
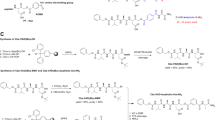
Caspases are enzymes that can cleave other proteins and control normal and abnormal cell death. Cancer cells generally lack apoptosis. In this research work, a computational approach has been adopted to design a promotor that targets the inactivated caspases particularly Pro-caspase-3 or caspase-7, which are the effector caspases that cleave the downstream substrates like lamin-A, ICAD and PARP. Out of the 38 anti-carcinomic compounds selected for the analysis, some of them are found to have positive charged substituents similar to the known drug; PAC1, which cleaves the safety catch mode that blocks the IETD active site. Site specific interactions of the proteins with these ligands were performed. From the interaction analysis, it was found that 3 compounds; Choline, Glaziovine, Dasatinib can effectively target caspases and activate them. It has been suggested that these compounds favor the activation of the effector caspase proteins, thereby giving a better option in cancer therapy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr, J.F.R., Winterford, C.M., Harmon, B.V.: Apoptosis Its Significance In Cancer And Cancer Therapy. Cancer 73(8) (April 15, 1994)
Kaufmann, H., Fusseneger, M.: Caspase Regulation At Molecular Level. Cell Engineering 4, 1–24 (2002) ISBN 978-1-4020
Khasibhatla, S., Tseng, B.: Why Target Apoptosis In Cancer Treatment? Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2, 573–580 (2003)
Putt, K.S., Chen, G.W., Pearson, J.M., Sandhorst, J.S., Hoagland, M.S., Kwon, J.-T., Hwang, S.-K., Jin, H., Churchwell, M.I., Cho, M.-H., Doerge, D.R., Helferich, W.G., Hergenrother, P.J.: Small-molecule activation of procaspase-3 to caspase-3 as a personalized anticancer strategy. Nature Chemical Biology 2(10) (October 2006)
LóPez-Lázaro, M.: Anticancer And Carcinogenic Properties Of Curcumin: Considerations For Its Clinical Development As A Cancer Chemopreventive And Chemotherapeutic Agent. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 52, 103–127 (2008)
Berman, H.M., Westbrook, J., Feng, Z., Gilliland, G., Bhat, T.N., Weissig, H., Shindyalov, I.N., Bourne, P.E.: The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Research 28(1), 235–242 (2000)
Thompson, J., Gibson, T., Higgins, D.: Multiple Sequence Alignment Using Clustalw And Clustalx. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics, ch. 2 Unit 2.3 (2002)
Gasteiger, E., Gattiker, A., Hoogland, C., Ivanyi, I., Appel, R.D., Bairoch, A.: Expasy: The Proteomics Server For In-Depth Protein Knowledge And Analysis. Nucleic. Acids Res. 31, 3784–3788 (2003)
Hulo, N., Bairoch, A., Bulliard, V., et al.: The Prosite Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Database Issue), D227–230 (2006)
Mackey, A.J., Haystead, T.A., Pearson, W.R.: Getting More from Less: Algorithms For Rapid Protein Identification With Multiple Short Peptide Sequences. Molecular And Cellular Proteomics 1(2), 139–147 (2002)
Geourjon, C., Deléage, G.: Sopma: A Self-Optimized Method for Protein Secondary Structure Prediction. Protein Eng. 7(2), 157–164 (1994)
Murzin, A., Brenner, S., Hubbard, T., Chothia, C.: Scop: A Structural Classification Of Proteins Database For The Investigation Of Sequences And Structures. J. Mol. Biol. 247(4), 536–540 (1995)
Jain, E., Bairoch, A., Duvaud, S., Phan, I., Redaschi, N., Suzek, B.E., Martin, M.J., Mcgarvey, P., Gasteiger, E.: Infrastructure For The Life Sciences: Design And Implementation Of The Uniprot Website. Bmc Bioinformatics 10, 136 (2009)
Accelrys Software Inc., Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 2.1, Accelrys Software Inc., San Diego (2007)
Wu, G., Robertson, D.H., III Brooks, C.L.: Detailed Analysis of Grid-Based Molecular Docking: A Case Study of CDOCKER - A CHARMm-Based MD Docking Algorithm. J. Comp. Chem. 24, 1549 (2003)
Kerns, D., Di, L.: Drug-like Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods: from ADME to Toxicity Optimization. Academic Press, London (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, M.S. et al. (2010). Designing a Promotor for a Novel Target Site Identified in Caspases for Initiating Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. In: Das, V.V., Vijaykumar, R. (eds) Information and Communication Technologies. ICT 2010. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 101. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15766-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15766-0_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15765-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15766-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)