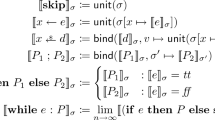Abstract
We present a constraint-based method for automatically generating quantitative invariants for linear probabilistic programs, and we show how it can be used, in combination with proof-based methods, to verify properties of probabilistic programs that cannot be analysed using existing automated methods. To our knowledge, this is the first automated method proposed for quantitative-invariant generation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Probabilistic Systems Group, http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~carrollm/probs
Bockmayr, A., Weispfenning, V.: Solving numerical constraints. In: Robinson, A., Voronkov, A. (eds.) Handbook of Automated Reasoning, vol. I, ch.12. vol. I, pp. 751–842. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (2001)
Celiku, O.: Mechanized Reasoning for Dually-Nondeterministic and Probabilistic Programs. PhD thesis, TUCS (2006)
Ciesinski, F., Baier, C.: LiQuor: A tool for qualitative and quantitative linear time analysis of reactive systems. In: Quantitative Evaluation of Systems (QEST), pp. 131–132. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2006)
Colón, M., Sankaranarayanan, S., Sipma, H.: Linear invariant generation using non-linear constraint solving. In: Hunt Jr., W.A., Somenzi, F. (eds.) CAV 2003. LNCS, vol. 2725, pp. 420–432. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Cousot, P.: Proving program invariance and termination by parametric abstraction, Lagrangian relaxation and semidefinite programming. In: Cousot, R. (ed.) VMCAI 2005. LNCS, vol. 3385, pp. 1–24. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cousot, P., Cousot, R.: Abstract interpretation: A unified lattice model for static analysis of programs by construction or approximation of fixpoints. In: Principles of Programming Languages (PoPL), pp. 238–252. ACM, New York (1977)
den Hartog, J., de Vink, E.P.: Verifying probabilistic programs using a Hoare like logic. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 13(3), 315–340 (2002)
Di Pierro, A., Wiklicky, H.: Concurrent constraint programming: towards probabilistic abstract interpretation. In: Gabbrielli, M., Pfenning, F. (eds.) Principles and Practice of Declarative Programming (PPDP), pp. 127–138. ACM, New York (2000)
Di Pierro, A., Wiklicky, H.: Measuring the precision of abstract interpretations. In: Lau, K. (ed.) LOPSTR 2000. LNCS, vol. 2042, pp. 147–164. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Dijkstra, E.W.: A Discipline of Programming. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1976)
Dolzmann, A., Sturm, T.: REDLOG: computer algebra meets computer logic. SIGSAM Bull. 31(2), 2–9 (1997)
Floyd, R.W.: Assigning meanings to programs. In: Schwartz, J.T. (ed.) Mathematical Aspects of Computer Science. Proc. Symp. Appl. Math., vol. 19, pp. 19–32. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1967)
Gulwani, S., Srivastava, S., Venkatesan, R.: Program analysis as constraint solving. Programming Language Design and Implementation (PLDI) 43(6), 281–292 (2008)
Hazewinkel, M.: Encyclopedia of Mathematics. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Hermanns, H., Wachter, B., Zhang, L.: Probabilistic CEGAR. In: Gupta, A., Malik, S. (eds.) CAV 2008. LNCS, vol. 5123, pp. 162–175. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Hinton, A., Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., Parker, D.: PRISM: A tool for automatic verification of probabilistic systems. In: Hermanns, H., Palsberg, J. (eds.) TACAS 2006. LNCS, vol. 3920, pp. 441–444. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Hoare, C.A.R.: An axiomatic basis for computer programming. Communications of the ACM 12(10), 576–580 (1969)
Hurd, J.: Formal Verification of Probabilistic Algorithms. PhD thesis, University of Cambridge (2002)
Hurd, J., McIver, A.K., Morgan, C.C.: Probabilistic guarded commands mechanised in HOL. Theoretical Computer Science 346(1), 96–112 (2005)
Kapur, D.: Automatically generating loop invariants using quantifier elimination. In: Deduction and Applications (2005)
Katoen, J.P., McIver, A.K., Meinicke, L.A., Morgan, C.C.: Linear-invariant generation for probabilistic programs: automated support for proof-based methods. Draft of this paper including its appendices [1, Katoen:10] (2010)
Kattenbelt, M.: Private communication (2010)
Kattenbelt, M., Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., Parker, D.: Abstraction refinement for probabilistic software. In: Jones, N.D., Müller-Olm, M. (eds.) VMCAI 2009. LNCS, vol. 5403, pp. 182–197. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Kozen, D.: Semantics of probabilistic programs. Jnl. Comp. Sys. Sciences 22, 328–350 (1981)
Legay, A., Murawski, A.S., Ouaknine, J., Worrell, J.: On automated verification of probabilistic programs. In: Ramakrishnan, C.R., Rehof, J. (eds.) TACAS 2008. LNCS, vol. 4963, pp. 173–187. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
McIver, A.K., Morgan, C.C.: Abstraction, Refinement and Proof for Probabilistic Systems. Monographs in Computer Science. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Monniaux, D.: Abstract interpretation of probabilistic semantics. In: Palsberg, J. (ed.) SAS 2000. LNCS, vol. 1824, pp. 322–339. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Morgan, C.C.: Proof rules for probabilistic loops. In: Jifeng, H., Cooke, J., Wallis, P. (eds.) BCS-FACS 7th Refinement Workshop, Workshops in Computing. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Podelski, A., Rybalchenko, A.: A complete method for the synthesis of linear ranking functions. In: Steffen, B., Levi, G. (eds.) VMCAI 2004. LNCS, vol. 2937, pp. 239–251. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Sankaranarayanan, S., Sipma, H.B., Manna, Z.: Non-linear loop invariant generation using Gröbner bases. In: Principles of Programming Languages (PoPL), pp. 318–329. ACM, New York (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Katoen, JP., McIver, A.K., Meinicke, L.A., Morgan, C.C. (2010). Linear-Invariant Generation for Probabilistic Programs: . In: Cousot, R., Martel, M. (eds) Static Analysis. SAS 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6337. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15769-1_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15769-1_24
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15768-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15769-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)