Abstract
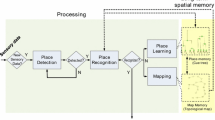
This paper presents a novel Topological Map of Place Cells model for autonomous robots. In such a model the robot acquires and stores perceptions using a basic memory provided by our proposed growing self-organizing map. Context sensitive cells aim to obtain Place Cells whose activation is dependent on a remembrance process that fires the recollection of stored memories from current robot perceptions. The map is a graph of interconnected and topologically organized Place Cells. The robots notion of localization is primary guided by the recollection process, while vestibular stimuli estimates and a historic of lastly visited places disambiguate conflicting simultaneously activated Place Cells. The results are promising.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ranvaud, R., Nehmzow, U.: The map concept in animal navigation. In: Proc. of Royal Institute of Navigation conference (2005)
O’Keefe, J., Dostrovsky, J.: The Hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely moving rat. Brain Research 34(1), 171–175 (1971)
Taube, J.S., Muller, R.U., Ranck, J.B.: Head-direction cells recorded from the post-subiculum in freely moving rats - II. Effects of Environmental Manipulations. J. of Neuroscience 10(2), 436–447 (1990)
Hafting, T., Fyhn, M., Molden, S., Moser, M.-B., Moser, E.I.: Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 436(7052), 801–806 (2005)
McNaughton, B.L., Battaglia, F.P., Jensen, O., Moser, E.I., Moser, M.-B.: Path integration and the neural basis of the “cognitive map”. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 7, 663–678 (2006)
Gruber, H.E., Voneche, J.J.: The essential Piaget. Basic Books, New York (1977)
Kuipers, B., Beeson, P., Modayil, J., Provost, J.: Bootstrap learning of foundational representations. Connection Science 18(2), 145–158 (2006)
OGRE 3D graphics engine, http://www.ogre3d.org
Scholl, B., Leslie, A.: Modularity, development and theory of mind. Mind and Language 14(1), 131–153 (1999)
McClamrock, R.: Holism without tears: local and global effects in cognitive processes. Philosophy of Science 56, 258–274 (1989)
Fodor, J.A.: The Mind Doesn’t Work That Way: The Scope and Limits of Computational Psycology. Theory & Psichology 13, 142–144 (2003)
Kuipers, B.: The spatial semantic hierarchy. J. Artificial Intelligence 119, 191–233 (2000)
Vasudevan, S., Nguyen, V., Siegwart, R.: Towards a cognitive probabilistic representation of space for mobile robots. In: Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Inf. Acquisition, ICIA 2006, pp. 353–359 (2006)
Weng, J.J., Hwang, W.-S.: From Neural Networks to the Brain: Autonomous Mental Development. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 15–31 (2006)
DalleMole, V.L., Araújo, A.F.R.: The growing Self-organizing surface Map. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, pp. 2061–2068 (2008)
DalleMole, V.L., Araújo, A.F.R.: Growing Self-Organizing Surface Map: learning a surface topology from a point cloud. Neural Computation 22(3), 689–729 (2010)
Bailey, R.R., Srinath, M.D.: Orthogonal moment features for use with parametric and nonparametric classifiers. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 18(4), 389–399 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
DalleMole, V.L., Araújo, A.F.R. (2010). A Novel Topological Map of Place Cells for Autonomous Robots. In: Diamantaras, K., Duch, W., Iliadis, L.S. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks – ICANN 2010. ICANN 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6353. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15822-3_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15822-3_37
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15821-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15822-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)