Abstract
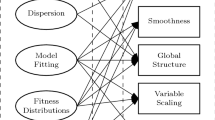
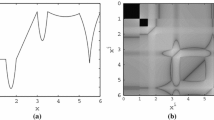
In this paper we extend a previously proposed randomized landscape generator in combination with a comparative experimental methodology to study the behaviour of continuous metaheuristic optimization algorithms. In particular, we generate landscapes with parameterised, linear ridge structure and perform pairwise comparisons of algorithms to gain insight into what kind of problems are easy and difficult for one algorithm instance relative to another. We apply this methodology to investigate the specific issue of explicit dependency modelling in simple continuous Estimation of Distribution Algorithms. Experimental results reveal specific examples of landscapes (with certain identifiable features) where dependency modelling is useful, harmful or has little impact on average algorithm performance. The results are related to some previous intuition about the behaviour of these algorithms, but at the same time lead to new insights into the relationship between dependency modelling in EDAs and the structure of the problem landscape. The overall methodology is quite general and could be used to examine specific features of other algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rardin, R.L., Uzsoy, R.: Experimental evaluation of heuristic optimization algorithms: A tutorial. Journal of Heuristics 7, 261–304 (2001)
Langdon, W., Poli, R.: Evolving problems to learn about particle swarm optimizers and other search algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 11(5), 561–578 (2007)
Gallagher, M., Yuan, B.: A general-purpose, tunable landscape generator. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 10(5), 590–603 (2006)
Gaviano, M., Kvasov, D., Lera, D., Sergeyev, Y.: Software for generation of classes of test functions with known local and global minima for global optimization. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 29(4), 469–480 (2003)
MacNish, C.: Towards unbiased benchmarking of evolutionary and hybrid algorithms for real-valued optimisation. Connection Science 19(4), 361–385 (2007)
Jones, D., Perttunen, C., Stuckman, B.: Lipschitzian optimization without the lipschitz constant. Journal of Optimization Theory and Application 79(1), 157–181 (1993)
Larrañaga, P., Lozano, J.A. (eds.): Estimation of Distribution Algorithms: A New Tool for Evolutionary Computation. Kluwer, Dordrecht (2002)
Pelikan, M., Goldberg, D.E., Lobo, F.: A survey of optimization by building and using probabilistic models. Computational Optimization and Applications 21(1), 5–20 (2002)
Hansen, N.: The CMA evolution strategy: a comparing review. In: Towards a New Evolutionary Computation, pp. 75–102 (2006)
Bosman, P., Grahl, J., Thierens, D.: Enhancing the Performance of Maximum–Likelihood Gaussian EDAs Using Anticipated Mean Shift. In: Rudolph, G., Jansen, T., Lucas, S., Poloni, C., Beume, N. (eds.) PPSN 2008. LNCS, vol. 5199, pp. 133–143. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
González, C., Lozano, J.A., Larrañaga, P.: Mathematical modelling of \(\textrm{UMDA}_c\) algorithm with tournament selection. Behaviour on linear and quadratic functions. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning (2002)
Grahl, J., Minner, S., Rothlauf, F.: Behaviour of UMDAc, with truncation selection on monotonous functions. In: Proc. Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2005), pp. 2553–2559. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2005)
Yuan, B., Gallagher, M.: A mathematical modelling technique for the analysis of the dynamics of a simple continuous EDA. In: Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 5734–5740. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2006)
Yuan, B., Gallagher, M.: Convergence analysis of \(\textrm{UMDA}_c\) with finite populations: a case study on flat landscapes. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, pp. 477–482. ACM, New York (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Morgan, R., Gallagher, M. (2010). When Does Dependency Modelling Help? Using a Randomized Landscape Generator to Compare Algorithms in Terms of Problem Structure. In: Schaefer, R., Cotta, C., Kołodziej, J., Rudolph, G. (eds) Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, PPSN XI. PPSN 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6238. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15844-5_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15844-5_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-15843-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-15844-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)