Abstract
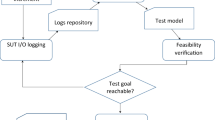
One aspect often neglected during the development of autonomous mobile robots is the systematic validation of their overall behavior. Especially large robots applied to real-world scenarios may cause injuries or even human death and must therefore be classified as safety-critical. In this paper, a generic approach to defining and executing purposeful test runs using domain-specific languages (dsls) is presented. Test cases can be defined in an appropriate test description language (first dsl). These test cases can be derived automatically using a model-based testing approach, for which a test model has to be created. Hence, a second dsl for the creation of the test model is presented. It is further shown how the generated test cases are automatically executed and evaluated. The paper concludes with the application of the approach to the autonomous off-road robot ravon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharygina, N., Browne, J., Xie, F., Kurshan, R., Levin, V.: Lessons learned from model checking a nasa robot controller. Form. Methods Syst. Des. 25(2-3), 241–270 (2004)
Kim, M., Kang, K.C.: Formal construction and verification of home service robots: A case study. In: Peled, D.A., Tsay, Y.-K. (eds.) ATVA 2005. LNCS, vol. 3707, pp. 429–443. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Lankenau, A., Meyer, O.: Formal methods in robotics: Fault tree based verification. In: Proc. Quality Week Europe, Brussels, Belgium (1999)
Lankenau, A., Röfer, T.: A safe and versatile mobility assistant. reinventing the wheelchair. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, 29–37 (2001)
Rosenblatt, J.: Damn: A distributed architecture for mobile navigation. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence 9, 339–360 (1997)
Goldberg, D., Mataric, M.: Design and evaluation of robust behavior-based controllers for distributed multi-robot collection tasks. Robot Teams: From Diversity to Polymorphism (2001)
Lüth, C., Krieg-Brückner, B.: Sicherheit in der künstlichen intelligenz. Künstliche Intelligenz 21(1), 51–52 (2007)
Prowell, S.: Using markov chain usage models to test complex systems. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, HICSS 2005, p. 318c (January 2005)
Hussain, T., Eschbach, R.: Statistical testing of iec 61499 compliant software components. In: Proceedings of INCOM 2009 (2009)
Prowell, S., Poore, J.: Foundations of sequence-based software specification 29(5), 417–429 (May 2003)
Lin, L., Prowell, S., Poore, J.: The impact of requirements changes on specifications and state machines. Softw. Pract. Exper. 39(6), 573–610 (2009)
Kloos, J., Eschbach, R.: Generating system models for a highly configurable train control system using a domain-specific language: A case study. In: Proceedings of A-MOST 2009 (2009)
Proetzsch, M., Luksch, T., Berns, K.: Development of complex robotic systems using the behavior-based control architecture iB2C. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 58(1) (2010)
Braun, T., Wettach, J., Berns, K.: A customizable, multi-host simulation and visualization framework for robot applications. In: 13th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR 2007), Jeju, Korea, August 21-24, pp. 1105–1110 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Proetzsch, M., Zimmermann, F., Eschbach, R., Kloos, J., Berns, K. (2010). A Systematic Testing Approach for Autonomous Mobile Robots Using Domain-Specific Languages. In: Dillmann, R., Beyerer, J., Hanebeck, U.D., Schultz, T. (eds) KI 2010: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. KI 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6359. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16111-7_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16111-7_36
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-16110-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-16111-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)