Summary
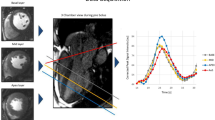
In this article we present our research into the subject of reducing the influence of noise on evaluation of perfusion parameters, such as CBF, CBV or MTT. Noise can be present on some pixels of study slices, therefore it can lead to artifacts in calculated concentration time curves and blur the final results.
To minimize influence from these factors we propose method that is different from commonly used. Generally noise reduction is done by filtering (smoothing, blurring), which is not always producing good results, as many information from image is lost. Therefore more effective is using the interpolation methods.
We have studied different interpolation techniques and compared them numerically. Tests have proven that using our method leads to better, more accurate estimation of perfusion parameters. It also seems that large window Sinc interpolation gives the best results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edelman, R.R., Siewert, B., Darby, D.G., Thagaraj, V., Nobre, A.C., Mesulam, M.M.: Qualitive Mapping of cerebral blood-flow and functional localization with echo-planar MR imaging and signal targeting with alternating radio-frequency. Radiology 192, 513–520 (1994)
Mihara, F., Kuwabara, Y., Tanaka, A., et al.: Reliability of mean transit time obtained using perfusion weighted MR imaging: comparision with positron emission tomography. Magn. Reson Imaging 20, 33–39 (2003)
Restrepo, L., Wityk, R.J., Grega, M., et al.: Diffusion and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the brain before and after coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. In: Stroke 2002, vol. 33, pp. 2909–2915 (2002)
Boxerman, J.L., Rosen, B.R., Weisskoff, R.M.: Signal-to-noise analysis of cerebral blood volume maps from dynamic NMR imaging studies. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 7, 528–537 (1997)
Kaneko, K., Kuwabara, Y., Mihara, F., et al.: Validation of the CBF, CBV, and MTT values by perfusion MRI in chronic occlusive cerebrovascular disease: a comparision with OPET. Academic Radiology 11(5), 489–497 (2004)
Wirestam, R., Anderson, L., Ostergaard, L., et al.: Assessment of regional blood flow by dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI using different deconvolution techniques. Magn. Reson. Med. 43, 691–700 (2000)
Ostergaard, L., Weiskoff, R.M., Chester, D.A., et al.: High resolution measurement of cerebral blood flow using intravascular tracer bolus passages Part I: Mathematical approach and statistical analysis. Magn. Reson. Med. 36, 715–736 (1996)
Bereczki, D., Wei, L., Otsuka, T., et al.: Hypercapnia slightly rises blood volume and sizably elevates flow velocity in brain microvessels. M. J. Physiol. 264, H1360-H1369 (1994)
Lehmann, T.M., Gönner, C., Spitzer, K.: Survey: Interpolation Methods in Medical Image Processing. IEEE Transactions on medical imaging 18(11) (1999)
Parker, J.A., Kenyon, R.V., Troxel, D.E.: Comparision of interpolating methods for image resampling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. MI-2, 31–39 (1983)
Beauchamp, K.G.: Signal Processing. George & Allen Unwin Ltd (1973)
Danielsson, P.E., Hammerin, M.: High accuracy rotation of images. Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing 54(4), 340–344 (1992)
Catmull, E., Rom, R.: A class of local interpolating splines. In: Barnhill, R.E., Riesenfeld, R.F. (eds.) Computer Aided Geometric Design, pp. 317–326. Academic Press, New York (1974)
Meijering, E.H.W.: Spline interpolation in medical imaging: comparison with other convolution-based approaches. In: Signal Processing X: Theories and Applications - Proceedings of EUSIPCO 2000, vol. IV, pp. 1989–1996 (2000)
Wolberg, G.: Digital Image Warping. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (1990)
Lanczos, C.: Discourse on Fourier Series. Oliver & Boyd, London (1966)
Thacker, N.A., Jackson, A., Moriarty, D., Vokurka, B.: Renormalised Sinc Interpolation, University of Manchester, Tina Memo No. 1999–005 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kartaszyński, R.H., Mikołajczak, P. (2010). Noise Influance Reduction in Estimation of CBF, CBV and MTT, MRI Perfusion Parameters. In: Choraś, R.S. (eds) Image Processing and Communications Challenges 2. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 84. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16295-4_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16295-4_26
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-16294-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-16295-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)