Abstract
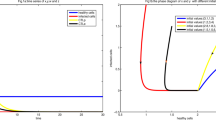
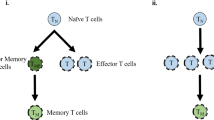
Immune memory can be regarded as an equilibrium state of immune network system with nonlinear behavior. The rapid response of immune systems to the second-time antigen is owing to the stable structure of memory state forming by a closed loop of the idiotypic immune network. A dynamical system is proposed which explains how the memory state is formed and stabilized in the immune network.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jerne, N.: Ann. Immunol. (Inst. Pasteur) 125C, 373 (1974)
Hoffman, G.W.: A theory of regulation and self-nonself discrimination in an immune network. Eor. J. Immunol. 5, 638–647 (1975)
Perelson, A.: Mathematical Approaches in Immunology. In: Andersson, S., et al. (eds.) Theory & Control of Dynamical Systems: Applications to Systems in Biology, pp. 200–230. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore (1992)
Parisi, G.: A Simple Model for the Immune Network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 87, 429–433 (1990)
Sonoda, T.: Formation and Stability of a Memory State in the Immune Network. J. Physical Society of Japan 61(4), 1408–1424 (1992)
Perelson, A. (ed.): Theoretical Immunology, Part One and Two, The Proceedings of the Theoretical Immunology Workshop. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1988)
Smith, D., Forrest, S., Perelson, A.: Immunological Memory is Associative, Artificial Immune Systems and Their Applications. In: 1999 The International Conference on the Multi-Agent Systems Workshop Notes, Kyoto, pp. 62–70 (1996)
Nielsen, K., White, R.: Nature 250, 235 (1974)
Seledtsov, V., Seledtsova, G.: A Pendular Mechanism for Maintenance of the Immune Memory. Medical Hypotheses 56(2), 160–162 (2001)
Farmer, J., Packard, N., Perelson, A.: THE Immune System, Adaptation, and Machine Learning. Physica 22D, 187–204 (1986)
Harada, K.: A Switching Memory Strategy in an Immune Network Model. In: Negoita, M.G., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds.) KES 2004. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3214, pp. 519–525. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Matzinger, P.: Memories Are Made of This? Nature 369, 605–606 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ou, CM., Ou, C.R. (2010). Immune Memory Mechanism Based on Cyclic Idiotypic Network. In: Pan, JS., Chen, SM., Nguyen, N.T. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. Technologies and Applications. ICCCI 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6423. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16696-9_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16696-9_45
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-16695-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-16696-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)