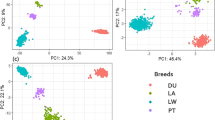
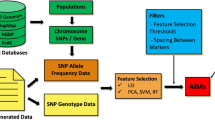
Abstract
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) can be used to identify the differences among populations. However, for high-level organisms, there are numerous number of SNPs distributed throughout entire of the genomes. Animal breeders can make use of these genetic markers to different subpopulations. For economical purpose, finding a minimum number of SNPs that can accurately identify different breeds is needed. In this paper, given a set of SNP genotyping samples, without knowing what breed a sample belong to (unlabeled samples), we developed a framework to classify these samples into different animal groups (breeds) based on their genotyping profiles. The proposed framework further identifies a small set of SNPs, called ancestry informative markers (AIMs) that can accurately classify these samples to these groups. The proposed framework adopted the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) technique, and Student’s t-test, to cluster unlabeled genotype data and determine AIMs, respectively. This unsupervised approach can avoid potential ascertainment biases due to mistakenly label some samples or having unlabeled data to be classified.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budowle, B., Van Daal, A.: Forensically Relevant SNP Classes. BioTechniques 44, 603–610 (2008)
Moore, J.H., Gilbert, J.C., Tsai, C.-T., Chiang, F.-T., Holden, T., Barney, N., White, B.C.: A flexible computational framework for detecting, characterizing and interpreting patterns of epistasis in genetic studies of disease susceptibility. J. Theor. Biol. 241, 252–261 (2006)
Pritchard, J.K., Donnelly, P.: Case-Control Studies of Association in Structured or Admixed Populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 60, 227–237 (2001)
Guinand, B., Topchy, A., Page, K.S., Burnham-Curtis, M.K., Punch, W.F., Scribner, K.T.: Comparisons of Likelihood and Machine Learning Methods of Individual Classification. J. Hered. 93, 260–269 (2002)
Park, J., Hwang, S., Lee, Y.S., Kim, S.C., Lee, D.: SNP@Ethnos: a Database of Ethnically Variant Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (Database issue), D711–D715 (2007)
Zhou, N., Wang, L.: Effective Selection of Informative SNPs and Classification on the HapMap Genotype Data. BMC Bioinformatics 8 (2007)
Rosenberg, N.A.: Algorithms for Selecting Informative Marker Panels for Population Assignment. J. Comput. Biol. 12, 1183–1201 (2005)
DeNise, S.K., Charteris, P., Rosenfeld, D.: Compositions, Methods and Systems for Inferring Bovine Breed, PatentStorm: Application: 10750622 (2005)
Patterson, N., Price, A.L., Reich, D.: Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2(12), e190 (2006)
Bovine Genome Project, http://www.hgsc.bcm.tmc.edu/projects/bovine/index.html
Pritchard, J.K., Stephens, M., Donnelly, P.: Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2), 945–959 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rodpan, A., Wangkumhang, P., Assawamakin, A., Prom-on, S., Tongsima, S. (2010). Unsupervised Algorithms for Population Classification and Ancestry Informative Marker Selection. In: Chan, J.H., Ong, YS., Cho, SB. (eds) Computational Systems-Biology and Bioinformatics. CSBio 2010. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 115. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16750-8_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16750-8_18
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-16749-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-16750-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)