Abstract
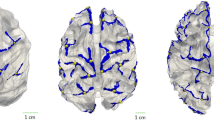
The variability in cortical morphology across subjects makes it difficult to develop a general atlas of cortical sulci. In this paper, we present a data-driven technique for automatically learning cortical folding patterns from MR brain images. A local image feature-based model is learned using machine learning techniques, to describe brain images as a collection of independent, co-occurring, distinct, localized image features which may not be present in all subjects. The choice of feature type (SIFT, KLT, Harris-affine) is explored with regards to identifying cortical folding patterns while also uncovering their group-related variability across subjects. The model is built on lateral volume renderings from the ICBM dataset, and applied to hemisphere classification in order to identify patterns of lateralization based on each feature type.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ono, M., et al.: Atlas of the Cerebral Sulci. Thieme Medical (1990)
Toga, A.W., et al.: Probabilistic approaches for atlasing normal and disease-specific brain variability. Anat. Embryol., 267–282 (2001)
Mangin, J., et al.: Object-Based Morphometry of the Cerebral Cortex. IEEE TMI (2004)
Mangin, J. et al.: A framework to study the cortical folding patterns. NeuroImage (2004)
Klein, A. et al.: Mindboggle: a scatterbrained approach to automate brain labeling. NeuroImage (2005)
Blezek, D.J., Miller, J.V.: Atlas stratification. In: Larsen, R., Nielsen, M., Sporring, J. (eds.) MICCAI 2006. LNCS, vol. 4190, pp. 712–719. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Baloch, S., et al.: An anatomical equivalence class based joint transformation-residual descriptor for morphological analysis. In: Karssemeijer, N., Lelieveldt, B. (eds.) IPMI 2007. LNCS, vol. 4584, pp. 594–606. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Toews, M., Arbel, T.: A Statistical Parts-based Appearance Model of Anatomical Variability. In: IEEE TMI, pp. 497–508 (2007)
Toews, M. et al.: Feature-Based Morphometry: Discovering Group-related Anatomical Patterns. NeuroImage (2009)
Toews, M., et al.: Automatically Learning Cortical Folding Patterns. In: IEEE ISBI, pp. 1330–1333 (2009)
Mazziotta, J., et al.: A probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain: International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM). Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 356(1412), 1293–1322 (2001)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. IJCV 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Tomasi, C., Shi, J.: Good Features to Track. In: CVPR, pp. 593–600 (1994)
Mikolajczyk, K., et al.: Scale and affine invariant interest point detectors. IJCV 60(1), 63–86 (2004)
Duchesnay, E., et al.: Classification from cortical folding patterns. IEEE TMI 26(4), 553–565 (2007)
Xu, C., et al.: A Spherical Map for Cortical Geometry. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Functional Mapping Human Brain, pp. 73–74 (1998)
Angenent, S., et al.: On the Laplace-Beltrami operator and brain surface flattening. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 18(8), 700–711 (1999)
Lyttelton, O., et al.: Positional and Surface Area Asymmetry of the Human Cerebral Cortex explored through automated surface-based analysis. Neuroimage (2009)
Foundas, A.L., et al.: Pars triangularis asymmetry and language dominance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93(2), 719–722 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rajalingham, R., Toews, M., Collins, D.L., Arbel, T. (2011). Exploring Cortical Folding Pattern Variability Using Local Image Features. In: Menze, B., Langs, G., Tu, Z., Criminisi, A. (eds) Medical Computer Vision. Recognition Techniques and Applications in Medical Imaging. MCV 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6533. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18421-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18421-5_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-18420-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-18421-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)