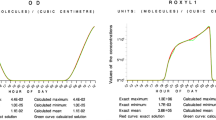
Abstract
A distributed software system for numerical simulations of atmospheric physicochemical processes is presented. It is a multi-layer Java based system for theoretical investigation of complex interactions of atmospheric trace gases and ice particles. The simulations are based on the fundamental theory of Langmuir adsorption and second Fick’s law applied for adsorption, desorption and diffusion processes. The system consists of three basic layers: (1) input/output interface layer, (2) dispatcher layer, (3) grid-based layer for simulations distributed over multiple machines. The core software module used in level (3) is based on previously published by us software prototype for simulations of adsorption, desorption and diffusion in a closed system and Flow Tube Reactor. The main task of the current distributed system is to derive numerical estimations of several significant constants: adsorption/desorption rates, ice entry rate, ice bulk diffusion coefficient and etc. The constants are estimated by comparison of experimental signals from a Flow Tube Reactor and simulations results from the system described in this paper. The difference between both curve profiles is minimized by an exhaustive search in a multi-dimensional parameter space which represents all possible values of the physicochemical constants. The dispatcher layer of the system defines several regions of the multi-dimensional parameter space. For each region, a separate task is configured and dispatched to a node from a computer GRID or cluster. The entire parameter space is searched in a parallel manner and after that all results are united in order to find the global minimum of the difference between experimental and simulated curves. The results are printed via the input/output software layer. Example kinetic simulations performed by the software system are presented and discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behr, P., Terziyski, A., Zellner, R.: Reversible Gas Adsorption in Coated Wall Flow Tube Reactors. Model Simulations for Langmuir Kinetics. Z. Phys. Chem. 218, 1307–1327 (2004)
Terziyski, A., Kochev, N.: Modelling Of Surface And Bulk Processes In The Atmosphere. Journal of International Scientific Publications, Issue Ecology and Safety 2, Part 1, 341–357 (2008)
Behr, P., Terziyski, A., Zellner, R.: Acetone Adsorption on Ice Surfaces in the Temperature Range T = 190-220 K: Evidence for Aging Effects Due to Crystallographic Changes of the Adsorption Sites. J. Phys. Chem. A 110(26), 8098–8107 (2006)
Modelling in ADvAnced Research Actions. MADARA, http://madara.orgchm.bas.bg
Somnitz, H.: Quantum chemical studies of the adsorption of single acetone molecules on hexagonal ice Ih and cubic ice Ic. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 1033–1042 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Terziyski, A.T., Kochev, N.T. (2011). Distributed Software System for Data Evaluation and Numerical Simulations of Atmospheric Processes. In: Dimov, I., Dimova, S., Kolkovska, N. (eds) Numerical Methods and Applications. NMA 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6046. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18466-6_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18466-6_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-18465-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-18466-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)