Abstract
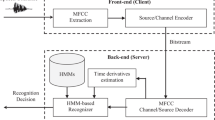
This paper investigates the contribution of formants and prosodic features like pitch and energy in Arabic speech recognition under real-life conditions. Our speech recognition system based on Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is implemented using the HTK Toolkit. The front-end of the system combines features based on conventional Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFFC), prosodic information and formants. The obtained results show that the resulting multivariate feature vectors lead to a significant improvement of the recognition system performance in noisy environment compared to cepstral system alone.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lévy, C., et al.: Comparison of several acoustic modeling techniques and decoding algorithms for embedded speech recognition systems. In: Workshop on DSP in Mobile and Vehicular Systems, Nagoya, Japan (2003)
Baudoin, G., Jardin, P.: Comparison de techniques paramétrisation spectrale pour la reconnaissance vocale en milieu bruité. Quatorzième colloque gretsi (1993)
Mary, L., Yegnanarayana, B.: Extraction and representation of prosodic features for language and speaker recognition. Speech Communication 50, 782–796 (2008)
Ezzaidi, H.: Discrimination Parole/ Musique et étude de nouveaux paramètres et modèles pour un système d’identification du locuteur dans le contexte de conférences téléphoniques, Thèse de doctorat. L’Université du Québec à Chicoutimi ; Département des Sciences Appliquées (2002)
Deleglise, P., et al.: Asynchronous integration of audio and visual sources in bi-model automatic speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the VIII European Signal Processing Conference, Trieste, Italy (1996)
Rogozan, A.: Etude de la fusion des données hétérogènes pour la reconnaissance automatique de la parole audio-visuelle. Doctoral thesis. L’université d’Orsay Paris XI (1999)
Mary, L., Yegnanarayana, B.: Extraction and representation of prosodic features for language and speaker recognition. Speech Communication 50, 782–796 (2008)
Dehak, N., et al.: Continuous Prosodic Features and Formant Modeling with Joint Factor Analysis for Speaker Verification. In: Proceedings of Interspeech 2007, pp. 1234–1237 (2007)
Rabiner, L.R.: A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. of the IEEE 77(2), 257–286 (1989)
Davis, S.B., Mermelstein, P.: Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Transaction on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 28(4), 357–366 (1980)
Fant, G.: Acoustic Theory of Speech Production. Mouton & Co., The Hague (1960)
Tremain, T.E.: The government standard Linear Predictive Coding algorithm: LPC10. Speech Technology Magazine 1, 40–49 (1982)
Rabiner, L.R.: On the Use of Autocorrelation Analysis for Pitch Detection. IEEE Transaction on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 25(1) (1977)
Youngand, S., Odell, J.: The HTK Book Version 3.3. Speech group, Engineering Department. Cambridge University, Cambridge (2005)
Amrouche, A.: Reconnaissance automatique de la parole par les modèles connexionnistes. Doctoral thesis, faculté d’électronique et d’informatique, USTHB (2007)
Varga, A.P., et al.: The NOISEX-92 study on the effect of additive noise on automatic speech recognition. In: NOISEX 1992, CDROM (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Amrous, A.I., Debyeche, M., Amrouche, A. (2011). Prosodic Features and Formant Contribution for Arabic Speech Recognition in Noisy Environments. In: Corchado, E., Snášel, V., Sedano, J., Hassanien, A.E., Calvo, J.L., Ślȩzak, D. (eds) Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications, 6th International Conference SOCO 2011. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 87. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19644-7_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19644-7_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-19643-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-19644-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)