Abstract
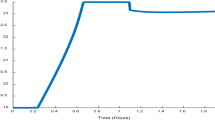
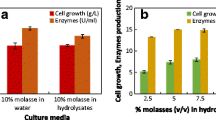
We used the software Optferm to model and optimize the bioprocess of escherichia coli fermentation, simulating the conditions of a fed-batch bioreactor. The results, obtained by employing different AI approaches, provided useful orientation for nutrient feed strategies for increased productivity. In conclusion, we believe in silico tools can perform a rapid and valid optimization of bioprocesses avoiding expensive experiments.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendes, R., Rocha, I., Ferreira, E., Rocha, M.: A Comparison of Algorithms for the Optimization of Fermentation Processes. In: 2006 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 2018–2025 (2006)
Yüzgeç, U., Türker, M., Hocalar, A.: On-line evolutionary optimization of an industrial fed-batch yeast fermentation process. ISA Transactions 48(1), 79–92 (2009)
Teusink, B., Wiersma, A., Jacobs, L., Notebaart, R.A., Smid, E.J.: Understanding the adaptive growth strategy of Lactobacillus plantarum by in silico optimisation. PLoS Computational Biology 5(6), e1000410 (2009)
Pinto Mariano, A., et al.: Optimization strategies based on sequential quadratic programming applied for a fermentation process for butanol production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 159(2), 366–381 (2009)
Kavanagh, J.M., Barton, G.W.: Productivity improvement of recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation via robust optimization. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering 31(2), 137–143 (2008)
Rocha, I., Ferreira, E., Veloso, A., Neves, J., Rocha, M.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Static and Dynamic Optimization of Fed-batch Fermentation Processes. In: Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms, pp. 288–291. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Rocha, O., Maia, P., Rocha, I., Rocha, M.: OPTFERM-A Computational Platform for the Optimization of Fermentation Processes. In: Presented at the European Simulation and Modelling Conference (ESM 2009), Leicester, UK, pp. 5–9 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Teixeira, T., Deusdado, S. (2011). Experiments on Computer Assisted Optimization of the Escherichia Coli Fermentation Process Using Optferm. In: Rocha, M.P., Rodríguez, J.M.C., Fdez-Riverola, F., Valencia, A. (eds) 5th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2011). Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol 93. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19914-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19914-1_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-19913-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-19914-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)