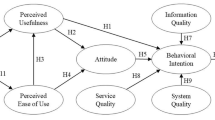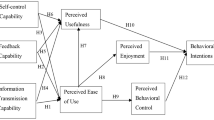Abstract
In an era of rapid change, with a need for lifelong learning, this study aimed to explore the behaviors of lifelong learning by proposing an integrated theoretical framework for the lifelong learners’ usage behavior on web-based e-learning. The research model draws on TAM and integrates with TPB to predict the lifelong learners’ intention to continue using e-learning. Subjects were randomly selected from the members of the SME Online University in Taiwan and analyzed using partial least squares structural model (PLS). Results showed that course flexibility, course quality, system functionality and system response significantly affect learners’ perceptions. Both the perceived usefulness and perceived ease-of-use have positive effects on users’ intentions of continued use of the e-learning website. Additionally, our research findings indicated that for lifelong learning, learners’ perceived behavioral control should be considered in the model for their planned behavior of e-learning activities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen, I.: The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 50, 179–211 (1991)
Anonymous: Ambient Insight Reports Strong US eLearning Market. Business Wire (2009)
Arbaugh, J.B.: Managing the On-Line Classroom: A Study of Technological and Behavioral Characteristics of Web-Based MBA Courses. Journal of High Technology Management Research 13, 203–223 (2002)
Barclay, D.W., Higgins, C.A., Thompson, R.: The Partial Least Squares (PLS) Approach to Causal Modeling: Personal Computer Adoption and Use as an Illustration. Tech. Stud. 2(2), 285–309 (1995)
Minshell, C., Butterworth, C., Henderson, J.: Occupational Health 61(3), 35 (2009)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison of Two Theoretical Models. Management Science 35(8), 982–1003 (1989)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. Journal Marketing Research 18, 39–50 (1981)
Fretty, P.: Go the Distance. PM Network 20(9), 16–21 (2006)
Lamont, J.: E-learning: Options for Delivery. KM World 17(5), 22–23 (2008)
Lee, M.C.: Explaining and Predicting Users’ Continuance Intention toward E-Learning: An Extension of the Expectation–Confirmation Model. Computers & Education 54(2), 506–516 (2009)
Liao, H. L., Chou, Y. J.: Factors Influencing Adult Learners’ Continued Use of E-Learning. In: 2010 Information Management Research and Application Conference (IMRAC) proceeding (2010)
Liu, S.H., Liao, H.L., Pratt, J.A.: Impact of Media Richness and Flow on E-Learning Technology Acceptance. Computers & Education 52, 599–607 (2009)
Nunnally, J.C.: Psychometric Theory. McGraw-Hill, New York (1978)
Pituch, K.A., Lee, Y.K.: The influence of system characteristics on e-learning use. Computers & Education 47, 222–244 (2006)
Plouffe, C.R., Hulland, J.S., Vandenbosch, M.: Research Report: Richness Versus Parsimony in Modeling Technology Adoption Decisions–Understanding Merchant Adoption of a Smart Card-Based Payment System. Information Systems Research 12(2), 208–222 (2001)
Schooley, C.: The ROI of E-learning. KM World 18(7), 12–13 (2009)
Sun, P.C., Tsai, R.J., Finger, G., Chen, Y.Y., Yeh, D.: What Drives a Successful E-Learning? An Empirical Investigation of the Critical Factors Influencing Learner Satisfaction. Computers & Education 50, 1183–1202 (2008)
Wixom, B.H., Todd, A.P.: A Theoretical Integration of User Satisfaction and Technology Acceptance. Information Systems Research 16(1), 85–102 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liao, HL., Liu, SH., Pi, SM., Chou, YJ. (2011). Factors Affecting Lifelong Learners’ Intention to Continue Using E-Learning Website: An Empirical Study. In: Luo, X., Cao, Y., Yang, B., Liu, J., Ye, F. (eds) New Horizons in Web-Based Learning - ICWL 2010 Workshops. ICWL 2010. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6537. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20539-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20539-2_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-20538-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-20539-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)