Abstract
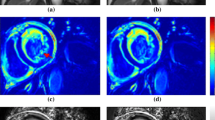
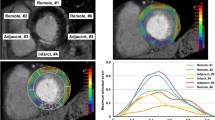
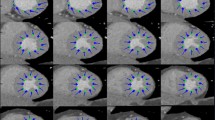
This paper presents an automated method for regional wall motion abnormality detection (RWMA) from rest and stress cardiac MRI. The automated RWMA detection is based on a statistical shape model of myocardial contraction trained on slice-based myocardial contours from in ED and ES. A combination of rigid and non-rigid registrations is introduced to align a patient shape to the normokinetic myocardium model, where pure contractility information is kept. The automated RWMA method is applied to identify potentially infarcted myocardial segments from rest–stress MRI alone.
In this study, 41 cardiac MRI studies of healthy subjects were used to build the statistical normokinetic model, while 12 myocardial infarct patients were included for validation. The rest–stress data produced a better separation between scar and normal segments compared to the rest–only data. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were increased by 34%, 30%, and 32%, respectively. The area under the ROC curve for the rest–stress data was improved to 0.87 compared to 0.63 for the rest–only data.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bookstein, F.L.: Principal Warps: Thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(6), 567–585 (1989)
Caiani, E.G., Toledo, E., et al.: Automated interpretation of regional left ventricular wall motion from cardiac magnetic resonance images. J. Cardiovasc Magn. Reson. 8(3), 427–433 (2006)
Dryden, I.L., Mardia, K.V.: Statistical shape analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Chichester (1998)
van der Geest, R.J., Buller, V.G., et al.: Comparison between manual and semiautomated analysis of left ventricular volume parameters from short-axis MR images. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 21(5), 756–765 (1997)
Herz, S.L., Ingrassia, C.M., et al.: Parameterization of left ventricular wall motion for detection of regional ischemia. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33(7), 912–919 (2005)
Heusch, G., Schulz, R., Rahimtoola, S.H.: Myocardial hibernation: a delicate balance. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288(3), H984–H999 (2005)
Hyvärinen, A., Karhunen, J., Oja, E.: Independent Component Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Chichester (2001)
Kaandorp, T.A.M., Bax, J.J., Schuijf, J.D., et al.: Head-to-head comparison between contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and dobutamine magnetic resonance imaging in men with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 93(12), 1461–1464 (2004)
Kachenoura, N., Redheuil, A., et al.: Evaluation of regional myocardial function using automated wall motion analysis of cine MR images: Contribution of parametric images, contraction times, and radial velocities. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 26(4), 1127–1132 (2007)
Kim, R.J., Wu, E., Rafael, A., et al.: The use of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to identify reversible myocardial dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 343(20), 1445–1453 (2000)
Mahrholdt, H., Klem, I., Sechtem, U.: Cardiovascular MRI for detection of myocardial viability and ischaemia. Heart 93(1), 122–129 (2007)
Qazi, M., Fung, G., et al.: Automated heart abnormality detection using sparse linear classifiers. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 26(2), 56–63 (2007)
Saraste, A., Nekolla, S., Schwaiger, M.: Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of myocardial infarction and viability. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 15(1), 105–117 (2008)
Sheather, S.J., Jones, M.C.: A reliable data-based bandwidth selection method for kernel density estimation. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 53(3), 683–690 (1991)
Suinesiaputra, A., Frangi, A.F., Kaandorp, T.A.M., Lamb, H.J., Bax, J.J., Reiber, J.H.C., Lelieveldt, B.P.F.: Automated detection of regional wall motion abnormalities based on a statistical model applied to multislice short-axis cardiac MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 28(4), 595–607 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Suinesiaputra, A. et al. (2011). Slice-Based Combination of Rest and Dobutamine–Stress Cardiac MRI Using a Statistical Motion Model to Identify Myocardial Infarction: Validation against Contrast-Enhanced MRI. In: Metaxas, D.N., Axel, L. (eds) Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart. FIMH 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 6666. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21028-0_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21028-0_33
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21027-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21028-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)