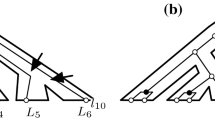
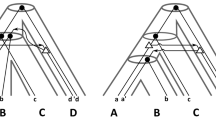
Abstract
Evolutionary methods are increasingly challenged by the fast growing resources of genomic sequence information. Fundamental evolutionary events, like gene duplication, loss, and deep coalescence, account more then ever for incongruence between gene trees and the actual species tree. Gene tree reconciliation is addressing this fundamental problem by invoking the minimum number of gene-duplication and losses that reconcile a gene tree with a species tree. Despite its promise, gene tree reconciliation assumes the gene trees to be correctly rooted and free of error, which severely limits its application in practice. Here we present a novel linear time algorithm for error-corrected gene tree reconciliation of unrooted gene trees. Furthermore, in an empirical study on yeast genomes we successfully demonstrate the ability of our algorithm to (i) reconcile (cure) error-prone gene trees, and (ii) to improve on more advanced evolutionary applications that are based on gene tree reconciliation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal, M.S., Burleigh, J.G., Eulenstein, O., Wehe, A.: Heuristics for the gene-duplication problem: A Θ(n) speed-up for the local search. In: Speed, T., Huang, H. (eds.) RECOMB 2007. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 4453, pp. 238–252. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Bansal, M.S., Eulenstein, O.: The multiple gene duplication problem revisited. Bioinformatics 24(13), i132–i138 (2008)
Behzadi, B., Vingron, M.: Reconstructing domain compositions of ancestral multi-domain proteins. In: Bourque, G., El-Mabrouk, N. (eds.) RECOMB-CG 2006. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 4205, pp. 1–10. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Bender, M.A., Farach-Colton, M.: The lca problem revisited. In: Gonnet, G.H., Panario, D., Viola, A. (eds.) LATIN 2000. LNCS, vol. 1776, pp. 88–94. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Bonizzoni, P., Della Vedova, G., Dondi, R.: Reconciling a gene tree to a species tree under the duplication cost model. Theoretical Computer Science 347(1-2), 36–53 (2005)
Chen, K., Durand, D., Farach-Colton, M.: NOTUNG: a program for dating gene duplications and optimizing gene family trees. J. Comput. Biol. 7(3-4), 429–447 (2000)
Durand, D., Halldorsson, B.V., Vernot, B.: A hybrid micro-macroevolutionary approach to gene tree reconstruction. J. Comput. Biol. 13(2), 320–335 (2006)
Eulenstein, O., Huzurbazar, S., Liberles, D.A.: Reconciling phylogenetic trees. In: Dittmar, Liberles (eds.) Evolution After Gene Duplication. Wiley, Chichester (2010)
Eulenstein, O., Mirkin, B., Vingron, M.: Duplication-based measures of difference between gene and species trees. J. Comput. Biol. 5(1), 135–148 (1998)
Fellows, M.R., Hallett, M.T., Stege, U.: On the multiple gene duplication problem. In: Chwa, K.-Y., Ibarra, O.H. (eds.) ISAAC 1998. LNCS, vol. 1533, pp. 347–356. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Goodman, M., Czelusniak, J., Moore, G.W., Romero-Herrera, A.E., Matsuda, G.: Fitting the gene lineage into its species lineage, a parsimony strategy illustrated by cladograms constructed from globin sequences. Systematic Zoology 28(2), 132–163 (1979)
Górecki, P., Tiuryn, J.: Inferring phylogeny from whole genomes. Bioinformatics 23(2), e116–e122 (2007)
Górecki, P., Tiuryn, J.: Urec: a system for unrooted reconciliation. Bioinformatics 23(4), 511–512 (2007)
Graur, D., Li, W.-H.: Fundamentals of Molecular Evolution. Sinauer Associates, 2 sub edition (2000)
Guigó, R., Muchnik, I.B., Smith, T.F.: Reconstruction of ancient molecular phylogeny. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 6(2), 189–213 (1996)
Hahn, M.W.: Bias in phylogenetic tree reconciliation methods: implications for vertebrate genome evolution. Genome Biology 8(7), R141+ (2007)
Ma, B., Li, M., Zhang, L.: From gene trees to species trees. SIAM Journal on Computing 30(3), 729–752 (2000)
Mirkin, B., Muchnik, I.B., Smith, T.F.: A biologically consistent model for comparing molecular phylogenies. J. Comput. Biol. 2(4), 493–507 (1995)
Notredame, C., Higgins, D.G., Jaap, H.: T-coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 302(1), 205–217 (2000)
Page, R.D.M.: Maps between trees and cladistic analysis of historical associations among genes, organisms, and areas. Systematic Biology 43(1), 58–77 (1994)
Page, R.D.M.: GeneTree: comparing gene and species phylogenies using reconciled trees. Bioinformatics 14(9), 819–820 (1998)
Sanderson, M.J., McMahon, M.M.: Inferring angiosperm phylogeny from EST data with widespread gene duplication. BMC Evolutionary Biology 7(Suppl 1), S3 (2007)
Sherman, D.J., Martin, T., Nikolski, M., Cayla, C., Souciet, J.-L., Durrens, P.: Gènolevures: protein families and synteny among complete hemiascomycetous yeast proteomes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Research 37(suppl 1), D550–D554 (2009)
Wehe, A., Bansal, M.S., Burleigh, G.J., Eulenstein, O.: DupTree: a program for large-scale phylogenetic analyses using gene tree parsimony. Bioinformatics 24(13), 1540–1541 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Górecki, P., Eulenstein, O. (2011). A Linear Time Algorithm for Error-Corrected Reconciliation of Unrooted Gene Trees. In: Chen, J., Wang, J., Zelikovsky, A. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 6674. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21260-4_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21260-4_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21259-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21260-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)