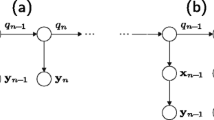
Abstract
A powerful approach for handling uncertainty in observations is to modify the statistical model of the data to appropriately reflect this uncertainty. For the task of noise-robust speech recognition, this requires modifying an underlying “clean” acoustic model to be representative of speech in a particular target acoustic environment. This chapter describes the underlying concepts of model-based noise compensation for robust speech recognition and how it can be applied to standard systems. The chapter will then consider important practical issues. These include i) acoustic environment noise parameter estimation; ii) efficient acoustic model compensation and likelihood calculation; and iii) adaptive training to handle multi-style training data. The chapter will conclude by discussing the limitations of the current approaches and research options to address them.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Acero. Acoustical and Environmental Robustness in Automatic Speech Recognition. Ph.D. thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, 1990.
A. Acero, L. Deng, T. T. Kristjansson, and J. Zhang. HMM adaptation using vector Taylor series for noisy speech recognition. In Proc. ICSLP, pages 869–872, Beijing, China, October 2000.
M. Afify, X. Cui, and Y. Gao. Stereo-based stochastic mapping for robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, 2007.
T. Anastasakos, J. McDonough, R. Schwartz, and J. Makhoul. A compact model for speaker-adaptive training. In Proc. ICSLP, 1996.
J. A. Arrowood and M. A. Clements. Using observation uncertainty in HMM decoding. In Proc. ICSLP, Denver, Colorado, September 2002.
S. F. Boll. Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions Audio Speech and Signal Processing, 27:113–120, 1979.
W. Chou. Maximum a posterior linear regression with elliptically symmetric matrix variate priors. In Proc. Eurospeech, 1999.
A. de la Torre, D. Fohr, and J.-P. Haton. Statistical adaptation of acoustic models to noise conditions for robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICSLP, pages 1437–1440, 2002.
L. Deng, A. Acero, M. Plumpe, and X. D. Huang. Large vocabulary speech recognition under adverse acoustic environments. In Proc. ICSLP, pages 806–809, Beijing, China, October 2000.
L. Deng, J. Droppo, and A. Acero. Enhancement of log mel power spectra of speech using a phase-sensitive model of the acoustic environment and sequential estimation of the corrupting noise. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 12:133–143, 2004.
V. V. Digalakis, D. Rtischev, and L. G. Neumeyer. Speaker adaptation using constrained estimation of Gaussian mixtures. IEEE Transactions Speech and Audio Processing, 3:357–366, 1995.
J. Droppo, A. Acero, and L. Deng. Uncertainty decoding with SPLICE for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, Orlando, Florida, May 2002.
F. Flego and M. J. F. Gales. Discriminative adaptive training with VTS and JUD. In Proc. ASRU, 2009.
F. Flego and M. J. F. Gales. Incremental predictive and adaptive noise compensation. In Proc. ICASSP, Taipei, Taiwan, 2009.
F. Flego and M. J. F. Gales. Adaptive Training and Noise Estimation for Model-Based Noise Compensation for ASR. Technical Report CUED/F-INFENG/TR653, University of Cambridge, 2010.
B. Frey, L. Deng, A. Acero, and T. T. Kristjansson. ALGONQUIN: Iterating Laplace’s method to remove multiple types of acoustic distortion for robust speech recognition. In Proc. Eurospeech, Aalbork, Denmark, September 2001.
M. J. F. Gales. Model-Based Techniques for Noise Robust Speech Recognition. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge University, 1995.
M. J. F. Gales. Maximum likelihood linear transformations for HMM-based speech recognition. Computer Speech and Language, 12, January 1998.
M. J. F. Gales. Semi-tied covariance matrices for hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 7:272–281, 1999.
M. J. F. Gales. Cluster adaptive training of hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions Speech and Audio Processing, 8:417–428, 2000.
M. J. F. Gales and F. Flego. Discriminative classifiers with adaptive kernels for noise robust speech recognition. Computer Speech and Language, 2010.
M. J. F. Gales and R. C. van Dalen. Predictive linear transforms for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. ASRU, pages 59–64, 2007.
M. J. F. Gales and P. C. Woodland. Mean and variance adaptation within the MLLR framework. Computer Speech and Language, 10:249–264, 1996.
M. J. F. Gales and S. J. Young. The application of hidden Markov models in speech recognition. Foundation and Trends in Signal Processing, 1(3):195–304, 2008.
R. A. Gopinath, M. J. F. Gales, P. S. Gopalakrishnan, S. Balakrishnan-Aiyer, and M. A. Picheny. Robust speech recognition in noise — performance of the IBM continuous speech recognizer on the ARPA noise spoke task. In Proc. ARPA Workshop on Spoken Language System Technology, pages 127–130, Austin, Texas, 1995.
R. A. Gopinath, B. Ramabhadran, and S. Dharanipragada. Factor analysis invariant to linear transformations of data. In Proc. ICSLP, pages 397–400, 1998.
H.-G. Hirsch and D. Pearce. The AURORA experimental framework for the evaluation of speech recognition systems under noisy conditions. In Proc. ASR, pages 181–188, September 2000.
Y. Hu and Q. Huo. Chinese Spoken Language Processing, chapter in An HMM Compensation Approach Using Unscented Transformation for Noisy Speech Recognition. Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, 2006.
X. D. Huang, A. Acero, and H. W. Hon. Spoken Language Processing. Prentice Hall, 2001.
Q. Huo and Y. Hu. Irrelevant variability normalization based HMM training using VTS approximation of an explicit model of environmental distortions. In Proc. Interspeech, pages 1042–1045, Antwerp, Belgium, 2007.
S. J. Julier and J. K. Uhlmann. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation. Proceedings of the IEEE, 92(3):401–422, 2004.
O. Kalinli, M.L. Seltzer, and A. Acero. Noise adaptive training using a vector taylor series approach for noise robust automatic speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, pages 3825–3828, Taipei, Taiwan, April 2009.
D. Kim and M. J. F. Gales. Adaptive training with noisy constrained maximum likelihood linear regression for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. Interspeech, Brighton, UK, 2009.
D. Kim and M. J. F. Gales. Noisy constrained maximum likelihood linear regression for noise robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions Audio Speech and Language Processing, 2010.
D. Y. Kim, C. K. Un, and N. S. Kim. Speech recognition in noisy environments using first-order vector Taylor series. Speech Communication, 24(1):39–49, June 1998.
T. T. Kristjansson. Speech Recognition in Adverse Environments: A Probabilistic Approach. Ph.D. thesis, Waterloo University, Waterloo, Canada, 2002.
L. Lee and R. C. Rose. Speaker normalisation using efficient frequency warping procedures. In ICASSP’96, Atlanta, 1996.
C. Leggetter and P. C. Woodland. Maximum likelihood linear regression for speaker adaptation of continuous density HMMs. Computer Speech and Language, 9, 1995.
V. Leutnant and R. Haeb-Umbach. An analytic derivation of a phase-sensitive observation model for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. Interspeech, pages 2395–2398, 2009.
J. Li, L. Deng, D. Yu, Y. Gong, and A. Acero. High-performance HMM adaptation with joint compensation of additive and convolutive distortions via vector Taylor series. In Proc. ASRU, pages 65–70, Kyoto, Japan, December 2007.
J. Li, L. Deng, D. Yu, Y. Gong, and A. Acero. HMM adaptation using a phase-sensitive acoustic distortion model for environment-robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, pages 4069–4072, April 2008.
H. Liao. Uncertainty Decoding for Noise Robust Speech Recognition. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge University, Cambridge, UK, sep 2007.
H. Liao and M. J. F. Gales. Joint uncertainty decoding for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. Interspeech, 2005.
H. Liao and M. J. F. Gales. Joint uncertainty decoding for robust large vocabulary speech recognition. Technical Report CUED/F-INFENG/TR552, University of Cambridge, 2006. Available from mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/ ∼ mjfg.
H. Liao and M. J. F. Gales. Adaptive training with joint uncertainty decoding for robust recognition of noisy data. In Proc. ICASSP, volume 4, pages 389–392, Honolulu, USA, April 2007.
H. Liao and M. J. F. Gales. Issues with uncertainty decoding for noise robust speech recognition. Speech Communication, 2008.
Y. Minami and S. Furui. A maximum likelihood procedure for a universal adaptation method based on HMM composition. In Proc. ICASSP, pages 129–132, 1995.
P. Moreno. Speech Recognition in Noisy Environments. Ph.D. thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, 1996.
L. Neumeyer and M. Weintraub. Probabilistic optimum filtering for robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, volume 1, pages 417–420, 1994.
D. Povey. Discriminative Training for Large Vocabulary Speech Recognition. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge University, 2003.
D. Povey, B. Kingsbury, L. Mangu, G. Saon, H. Soltau, and G. Zweig. fMPE: Discriminatively trained features for speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, Philadelphia, 2005.
L. R. Rabiner. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77(2):257–286, February 1989.
B. Raj and R. Stern. Missing feature approaches in speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 22(5):101–116, 2005.
C. K. Raut, T. Nishimoto, and S. Sagayama. Maximum likelihood based HMM state filtering approach to model adaptation for long reverberation. In Proc. ASRU, 2005.
D. Rubin and D. Thayer. EM algorithms for ML factor analysis. Psychometrika, 47(1):69–76, March 1982.
S. Sagayama, Y. Yamaguchi, S. Takahashi, and J. Takahashi. Jacobian approach to fast acoustic model adaptation. In Proc. ICASSP, 1997.
A. Sankar and C.-H. Lee. A maximum-likelihood approach to stochastic matching for robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 4:190–202, May 1996.
M. Seltzer, K. Kalgaonkar, and A. Acero. Acoustic model adaptation via linear spline interpolation for robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, 2010.
M. Seltzer, B. Raj, and R. Stern. A Bayesian framework for spectrographic mask estimation for missing feature speech recognition. Speech Communication, 43(4):379–393, 2004.
Y. Shinohara and M. Akamine. Bayesian feature enhancement using a mixture of unscented transformations for uncertainty decoding of noisy speech. In Proc. ICASSP, pages 4569–4572, 2009.
V. Stouten, H. van Hamme, and P. Wambacq. Accounting for the uncertainty of speech estimates in the context of model-based feature enhancement. In Proc. ICSLP, volume I, pages 105–108, Jeju Island, Korea, October 2004.
V. Stouten, H. van Hamme, and P. Wambacq. Effect of phase-sensitive environment model and higher order VTS on noisy speech feature enhancement. In Proc. ICASSP, volume I, pages 433–436, Philadelphia, USA, March 2005.
R. C. van Dalen, F. Flego, and M. J. F. Gales. Transforming features to compensate speech recogniser models for noise. In Proc. Interspeech, 2009.
R. C. van Dalen and M. J. F. Gales. Extended VTS for noise-robust speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, Taipei, Taiwan, 2009.
R. C. van Dalen and M. J. F. Gales. Asymptotically exact noise-corrupted speech likelihoods. In Proc. Interspeech, 2010.
A. P. Varga, R. K. Moore, J. Bridle, K. Ponting, and M. Russel. Noise compensation algorithms for use with hidden Markov model based speech recognition. In Proc. ICASSP, 1988.
H. Xu, M. J. F. Gales, and K. K. Chin. Improving joint uncertainty decoding performance by predictive methods for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. ASRU, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gales, M.J.F. (2011). Model-Based Approaches to Handling Uncertainty. In: Kolossa, D., Häb-Umbach, R. (eds) Robust Speech Recognition of Uncertain or Missing Data. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21317-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21317-5_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21316-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21317-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)